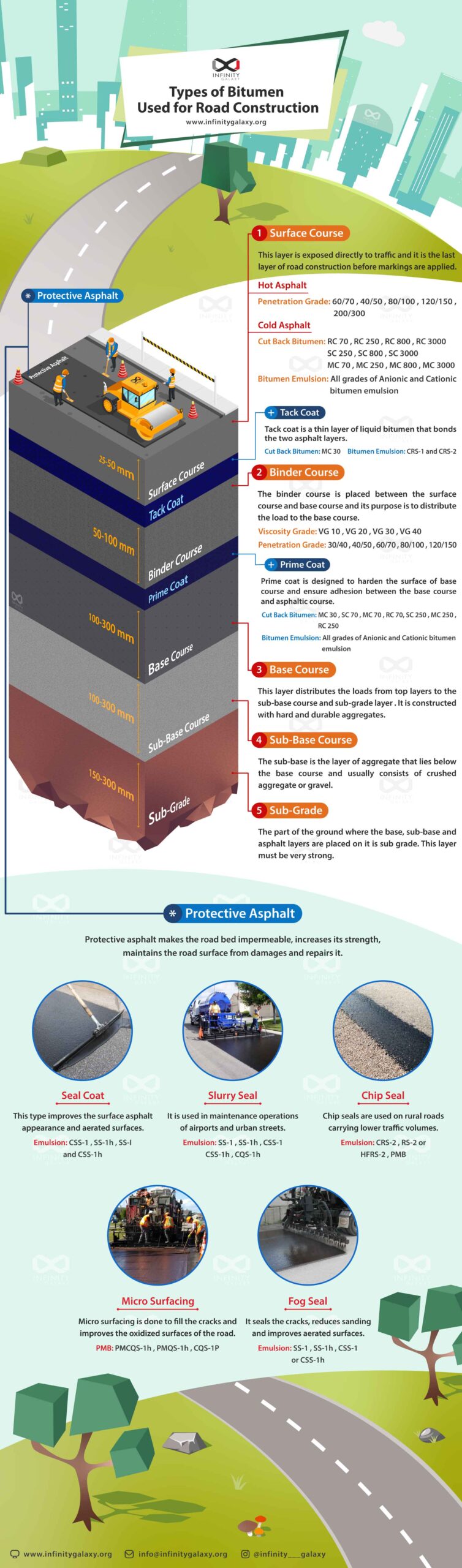
There exist different types of road pavements. Flexible Pavement and concrete pavement are the most common.
In flexible pavement, the bitumen plays a significant role in each layer. This type of pavement consists of different main layers and sub layers.
The main layers are surface course, base course and sub base course. The sub layers are tack coat, binder course and prime coat.
In the post below, we have clarified each layer and explained about the bitumen grades that can be used in them.
Main Layers of a Flexible Pavement
Surface Course
This layer is the top main layer of a road. It is exposed directly to the traffic. Generally, hot mix asphalt can be applied on this layer. In the hot asphalt it is possible to use different types of pure bitumen including:
- Penetration Grade Bitumen
- Viscosity Grade Bitumen
These types of pure bitumen are produced in the refinery. These are the output of a vacuum distillation tower. Different grades of these two types of bitumen that can be used in the HMA (Hot Mix Asphalt) are:
- Penetration Grades: 30/40, 40/50, 60/70, 80/100
- Viscosity Grades: VG10, VG20, VG30, VG40
Base Course
This is the second main layer of a flexible pavement. The loads and tension from the surface course will transfer to this layer. Altogether, the base course is made of different types of aggregates, but sometimes it is probable to use the bitumen in this layer.
Sub Base Course
Sub base course is like a foundation for a flexible pavement. The surface course and base course are placed on the sub base course. This layer has no bitumen.
In the above we had a summary of the main layer of a road. But now we are going to explain more about the layers which the bitumen is used in.
Sub Layers of a Flexible Pavement
Tack Coat
Tack coat is placed between the surface course and binder course. These two layers are made of asphalt with bitumen used in them. The function of the tack coat is to bond these two asphalt layers to each other.
The type of bitumen that can be used in the layer is liquid bitumen. Generally, there two types of liquid bitumen:
- Bitumen Emulsion
- Cut Back Bitumen
Bitumen emulsion is a type of liquid bitumen which consists of bitumen, water and emulsifier. But cut back bitumen is a type of bitumen that consists of bitumen and a petroleum based solvent.
These two types of liquid bitumen have their own grades. For example, bitumen emulsion is classified into slow setting, medium setting and rapid setting types. Or cut back bitumen is classified into slow curing, medium curing and rapid curing.
In the tack coat, the most common types of bitumen emulsion that are used are as below:
- CRS-1 and CRS-2
And the cut back bitumen grades that can be used in tack coat are:
- MC30, MC70, MC 250 etc.
It should be noted that in many countries using the cut back bitumen is banned. It seems since this bitumen causes cancer due to its petroleum based solvent. So the bitumen emulsion is highly recommended and highly used in many countries instead of the cut back bitumen.
Binder Course
The binder course transfers and distributes the load from the above layer to the base course. This layer is placed between the surface course and base course.
Same as surface course, different types of pure bitumen can be used in this layer including bitumen penetration grades like 30/40, 40/50, 60/70, 80/10 and bitumen viscosity grades like VG10, VG20, VG30 and VG40.
Besides these pure bitumen, there are also two other types of bitumen that can be used in the road construction as an additive. These types of bitumen are oxidized bitumen and natural bitumen which we call gilsonite.
Prime Coat
Prime coat is a layer which seals the base course surface and penetrates into it. Same as tack coat, the liquid bitumen can be used in this layer.
All grades of bitumen emulsion are suitable to use in this layer. And different types of cut back bitumen like SC 70, SC 250, RC 70, RC 250, MC 30, MC 70 and MC 250 can be used in the prime coat.
Protective Asphalts
Besides these layers of a flexible pavement, there are different types of protective asphalts that are applied on the road surface.
These protective asphalts maintain the road surface, make it impermeable and prevent erosion of the surface course.
The main advantage of protective asphalts is their low price. Because, the main component in these asphalts is liquid bitumen, which has a lower price than other types of bitumen.
Different types of bitumen emulsion and cutback bitumen can be used in these asphalts.
In the Infographic below which is prepared by one of the international bitumen suppliers, Infinity Galaxy, you can read more details about the types of bitumen grades that are used in road construction.