A commercial building refers to a structure that is primarily designed and used for business, retail, or industrial purposes rather than for residential purposes. These Commercial Building are intended to facilitate various types of commercial activities, which can include selling products or services, conducting business operations, providing office spaces, accommodating manufacturing processes, and more.

Commercial buildings come in various sizes and styles, ranging from small shops and offices to large warehouses and skyscrapers. Commercial Building are typically equipped with features and amenities that cater to the needs of businesses, such as office spaces, meeting rooms, retail display areas, storage facilities, and sometimes specialized infrastructure like industrial machinery.
The design and layout of commercial buildings can vary greatly based on their intended use. For instance, a shopping mall would have multiple retail spaces, common areas, and food courts, while an industrial building might have large open spaces for manufacturing equipment and storage.
Commercial buildings play a crucial role in the economy by providing spaces for businesses to operate, generate revenue, and contribute to job creation. Commercial Building are a key part of urban development and city landscapes, shaping the overall appearance and functionality of urban areas.
Contents
Different Types of Commercial Building
- Office Buildings
- Retail Buildings
- Industrial Buildings
- Hospitality Buildings
- Medical Buildings
- Educational Buildings
- Recreational buildings
Office Buildings
An office building is a type of Commercial Building structure designed and constructed primarily to facilitate various administrative, professional, and business-related activities. It serves as a space where employees and organizations carry out tasks, conduct meetings, collaborate on projects, and manage their operations. Office buildings come in various sizes and designs, ranging from small single-story buildings to towering skyscrapers in urban centers.
Key features and aspects of Office buildings:
Workspaces: Office buildings include a variety of workspaces to accommodate different needs. These can range from open-plan areas with shared desks to private offices for managers and executives.
Meeting Rooms: Different sizes of meeting rooms are often available for team discussions, presentations, and client meetings. Some office buildings even have specialized conference facilities for larger gatherings.
Common Areas: Many modern office buildings incorporate communal spaces like break rooms, cafeterias, and lounges where employees can relax, socialize, and recharge.
Amenities: Depending on the building’s design and purpose, there might be amenities such as fitness centers, wellness rooms, and even childcare facilities to support employees’ well-being.
Technological Infrastructure: Office buildings are equipped with essential technology, including internet connectivity, phone lines, and other communication systems to ensure smooth operations.
Security: Security measures like access control systems, surveillance cameras, and secure entrances are often in place to protect both the building’s occupants and valuable assets.
Energy Efficiency: Many modern office buildings incorporate sustainable design elements to minimize energy consumption, such as energy-efficient lighting, HVAC systems, and eco-friendly construction materials.
Location: The location of an office building is crucial, often being chosen based on factors like proximity to business districts, transportation hubs, and amenities.
Interior Design: The interior layout and design of an office building are carefully planned to foster productivity, collaboration, and comfort. This includes considerations for lighting, ergonomic furniture, and overall aesthetics.
Flexible Spaces: Some office buildings incorporate flexible layouts to adapt to changing work dynamics, such as hot desking, co-working spaces, and the ability to rearrange furniture as needed.
High-Rise vs. Low-Rise: Office buildings can be high-rise skyscrapers in city centers, offering spectacular views and centralized locations, or low-rise structures in suburban areas.
Office buildings play a pivotal role in the business world by providing organizations with spaces to carry out their operations efficiently. The design and features of an office building are often tailored to the specific needs of the businesses and employees that will inhabit them.
Also Read: Vertical Green Building: Revolutionizing Sustainability in Urban Architecture
Example of Office Buildings
One World Trade Center, New York City
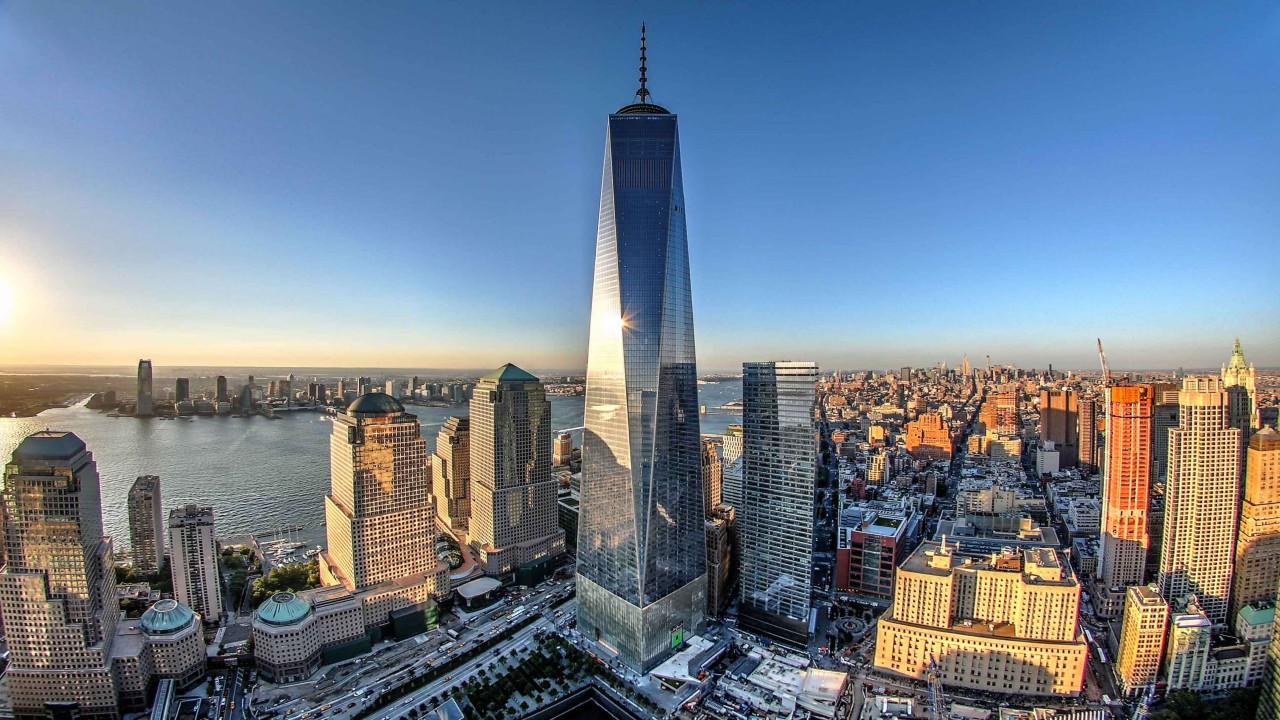

One World Trade Center, commonly referred to as the Freedom Tower, is a prominent office building located in Lower Manhattan, New York City. It stands as a symbol of resilience and a testament to the city’s strength after the tragic events of September 11, 2001.
Retail Buildings
Retail buildings are Commercial Building structures specifically designed to house businesses engaged in selling products and services directly to consumers. These Commercial Building are tailored to provide an attractive and functional environment for customers to browse, shop, and make purchases. Retail buildings come in various forms and sizes, each catering to different types of retail businesses and their unique requirements.
Key aspects of Retail buildings:
Storefront Design: Retail buildings often feature eye-catching storefronts with large windows, signage, and displays to entice passersby and showcase products.
Layout and Shelving: The interior layout is designed to guide customers through the store while maximizing product exposure. Shelving, racks, and displays are strategically positioned to showcase merchandise effectively.
Display Areas: Retail buildings include dedicated spaces for product displays, allowing businesses to showcase their offerings in an organized and appealing manner.
Checkout Counters: Typically located near the exit, checkout counters provide space for customers to finalize their purchases and interact with sales associates.
Aisle Design: Aisles are designed to facilitate customer flow, providing easy access to various sections of the store and optimizing space for both customers and products.
Visual Merchandising: Retail buildings often incorporate techniques of visual merchandising to create appealing displays that attract attention and encourage purchasing.
Lighting: Adequate lighting is essential to showcase products and create a pleasant shopping atmosphere. Different areas of the store might have varying lighting schemes to set different moods.
Branding and Interior Design: Retail buildings often reflect the brand identity of the business, incorporating specific colors, materials, and design elements to create a cohesive and memorable shopping experience.
Product Storage: Retail buildings have storage areas, often located behind the retail space, to manage inventory efficiently and restock shelves as needed.
Customer Amenities: Depending on the type of retail, there might be fitting rooms, restrooms, seating areas, and even customer service desks to enhance the shopping experience.
Security Measures: Retail buildings incorporate security measures such as surveillance cameras, anti-theft devices, and trained personnel to prevent theft and ensure customer safety.
Types of Retail Buildings: Retail buildings can include department stores, shopping malls, standalone boutiques, outlets, supermarkets, and specialty stores.
Retail buildings play a crucial role in the consumer economy by providing spaces for businesses to showcase and sell their products to the public. The design and layout of these buildings are carefully planned to create an environment that encourages customers to explore, engage, and make purchases.
Also Watch: North Sea Protection Works in the Netherlands: Exploring the Dutch Coastline
Example of Retail Buildings
The Grove, Los Angeles, California
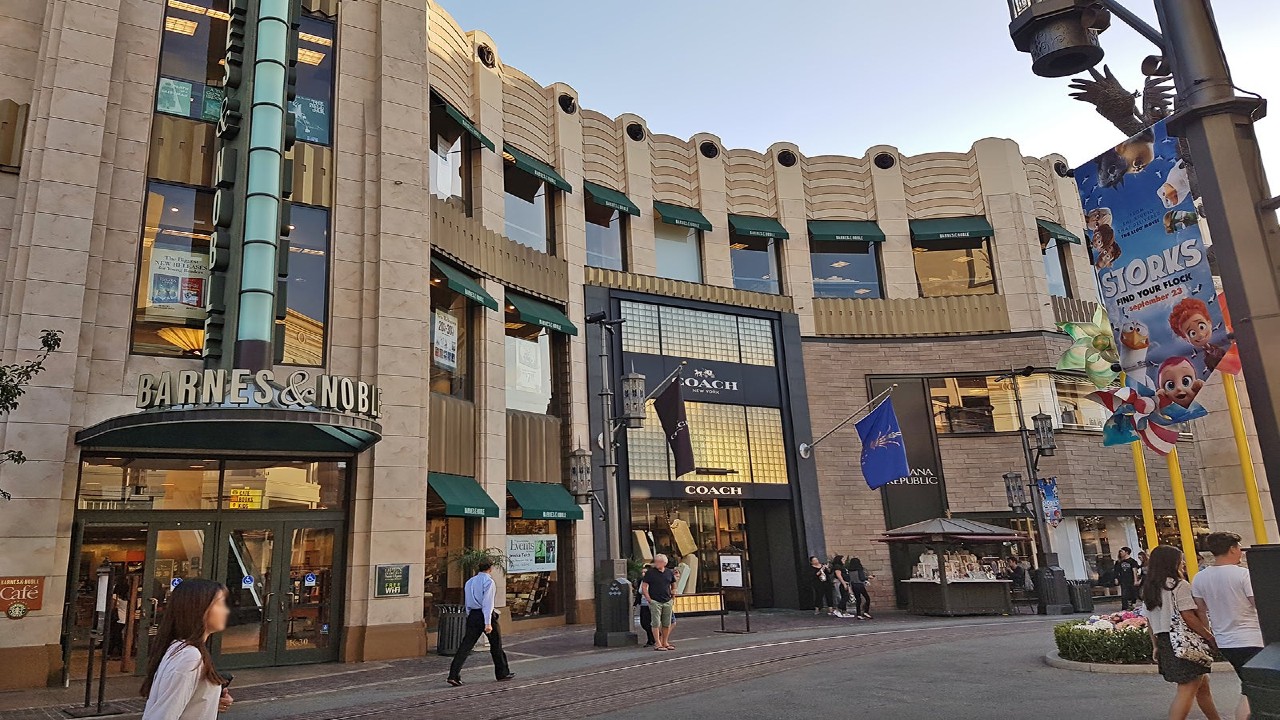

The Grove is a renowned retail and entertainment complex located in the heart of Los Angeles, California. It exemplifies the concept of a modern retail building that goes beyond shopping to create a vibrant and engaging experience for visitors.
Industrial Buildings
Industrial buildings are specialized Commercial Building structures designed to house manufacturing, production, storage, and distribution activities. These Commercial Building are tailored to accommodate the specific needs of industries that involve the processing of raw materials, the assembly of products, or the storage of goods. Industrial buildings come in various sizes and configurations, each catering to different types of industrial processes.
Key features of industrial buildings:
Functionality: Industrial buildings are designed to optimize workflows and operational efficiency. Layouts are carefully planned to facilitate the movement of materials, equipment, and personnel.
Open Space: Many industrial buildings have large, open floor plans to accommodate machinery, assembly lines, and other production processes. These spaces provide flexibility for various manufacturing activities.
Ceiling Height: Industrial buildings often feature high ceilings to accommodate large machinery, storage racks, and tall equipment. This vertical space is essential for certain manufacturing operations.
Loading Docks: Loading and unloading areas, such as loading docks and ramps, are incorporated into the design to streamline the transportation of raw materials and finished products.
Crane Systems: Some industrial buildings are equipped with overhead crane systems to move heavy materials and products efficiently within the facility.
Ventilation and Air Quality: Depending on the type of industry, ventilation systems may be installed to regulate air quality, temperature, and humidity, especially in environments that involve chemicals or pollutants.
Safety Measures: Industrial buildings prioritize safety, often including features such as fire suppression systems, emergency exits, and proper lighting to ensure a secure working environment.
Storage Space: Warehousing and storage areas are common in industrial buildings to house raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods before distribution.
Specialized Equipment: Industrial buildings may include specialized infrastructure like cooling systems for food processing, cleanrooms for electronics manufacturing, or ventilation for chemical production.
Energy Efficiency: Many modern industrial buildings incorporate energy-efficient lighting, HVAC systems, and insulation to reduce operating costs and environmental impact.
Zoning and Regulations: Industrial buildings must comply with local zoning and safety regulations, which can vary based on the type of industry and the location of the building.
Types of Industrial Buildings: Industrial buildings encompass various industries, including manufacturing plants, factories, warehouses, distribution centers, refineries, food processing facilities, and more.
Industrial buildings are vital to the production and distribution of goods that support economies and societies. Their designs are tailored to accommodate the specific needs of the industry they serve, with a focus on efficiency, safety, and functionality.
Also Read: 12 Types of Glass Used in Building Construction and Design
Example of Industrial Buildings
Tesla Gigafactory, Shanghai, China
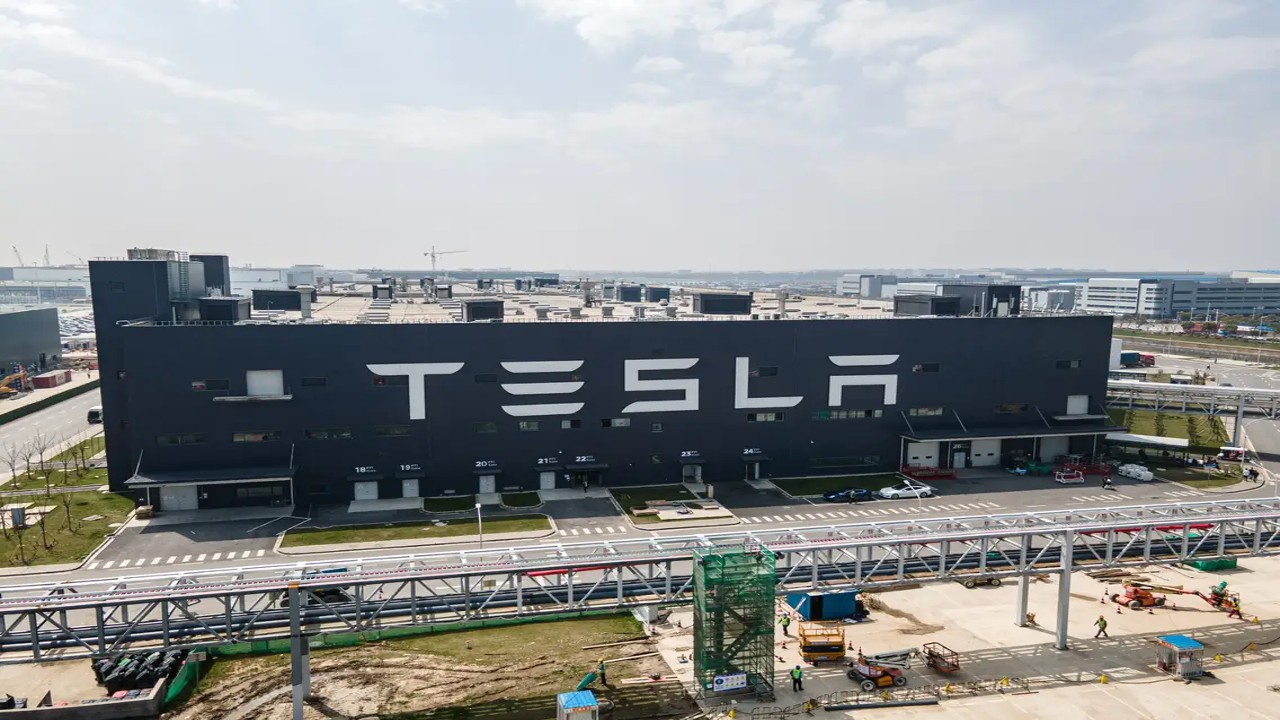

The Tesla Gigafactory in Shanghai, China, is a prime example of an advanced industrial building that supports the manufacturing of electric vehicles (EVs) on a massive scale. It showcases the integration of technology, sustainability, and efficient production processes.
Hospitality Buildings
Hospitality buildings are Commercial Building structures designed to provide accommodations, services, and amenities to travelers, tourists, and guests. These Commercial Building are dedicated to offering a comfortable and enjoyable experience for individuals and groups looking for temporary lodging and various hospitality services. Hospitality buildings include a range of facilities, from hotels and resorts to motels and lodges.
Key features of hospitality buildings:
Guest Rooms: The primary function of hospitality buildings is to provide guest rooms or suites where visitors can stay overnight. These rooms are equipped with beds, furnishings, and amenities to ensure a comfortable stay.
Lobby and Reception: Hospitality buildings often have a welcoming lobby or reception area where guests check in, receive assistance from staff, and gather information about the facilities.
Amenities: Depending on the type and class of the hospitality building, there can be a variety of amenities:
- Restaurants and Bars: On-site dining options, including restaurants, cafes, and bars, offer guests convenient meal choices.
- Swimming Pools and Spas: Many hospitality buildings feature swimming pools, hot tubs, and spa facilities for relaxation and leisure.
- Fitness Centers: Some buildings have fitness facilities equipped with exercise equipment for guests to stay active during their stay.
- Business Centers: For business travelers, hospitality buildings might provide business centers with office equipment and meeting rooms.
- Conference Facilities: Larger hospitality buildings may have conference rooms and event spaces for meetings, conferences, and special events.
Interior Design: Hospitality buildings often feature inviting and comfortable interior design, reflecting the ambiance and brand identity of the establishment.
Room Service: Many hospitality buildings offer room service, allowing guests to order food and beverages to their rooms for added convenience.
Housekeeping Services: Regular housekeeping ensures that guest rooms and common areas are clean and well-maintained throughout a guest’s stay.
Security: Security measures, such as keycard access systems and surveillance cameras, are put in place to ensure the safety of guests and their belongings.
Location: The location of hospitality buildings is often chosen strategically, considering proximity to tourist attractions, transportation hubs, and business districts.
Variety of Accommodations: Hospitality buildings can provide various types of accommodations, from standard rooms to suites, villas, and even serviced apartments.
Customer Service: Well-trained staff provide hospitality services, assisting guests with their needs, inquiries, and special requests.
Types of Hospitality Buildings: These include:
- Hotels: Ranging from budget hotels to luxury hotels, catering to various levels of service and comfort.
- Resorts: Large properties that offer a range of amenities and recreational facilities.
- Motels: Generally located along highways, offering convenient overnight accommodations for travelers.
- Bed and Breakfasts: Smaller establishments that provide a cozy and personalized experience.
- Inns and Lodges: Often located in scenic areas, offering a more relaxed and rustic atmosphere.
Hospitality buildings play a significant role in the travel and tourism industry, providing a home away from home for travelers while contributing to local economies and cultural experiences.
Example of Hospitality Buildings
Burj Al Arab, Dubai, United Arab Emirates
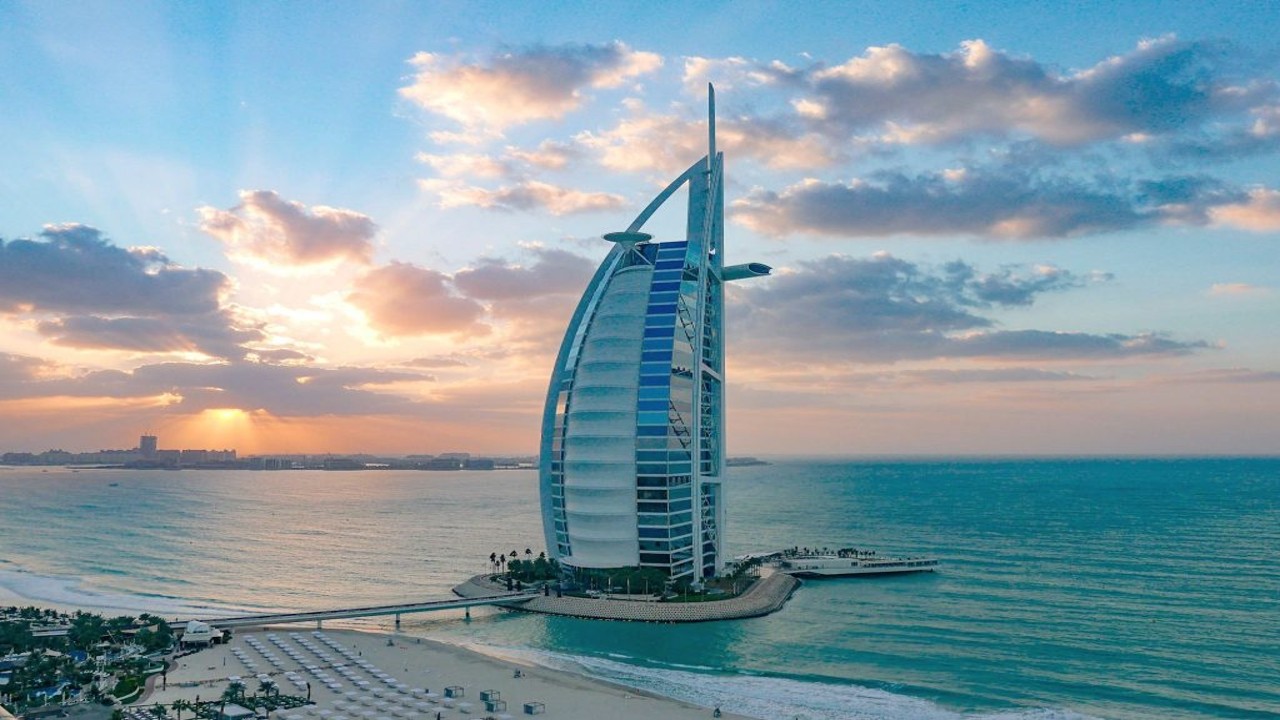

The Burj Al Arab in Dubai is an iconic hospitality building that redefines luxury and extravagance in the realm of hotels. This stunning structure stands as a symbol of opulence and offers an unparalleled experience for its guests.
Medical Buildings
Medical buildings are specialized Commercial Building structures designed to provide healthcare services, medical treatment, and related activities. These Commercial Building serve as facilities where patients receive medical care, consultations, diagnoses, surgeries, and various healthcare services. Medical buildings encompass a wide range of healthcare settings, from hospitals and clinics to medical offices and specialized treatment centers.
Key features of medical buildings include:
Patient Care Areas: Medical buildings are equipped with spaces dedicated to patient care, including examination rooms, treatment areas, and patient wards in the case of hospitals.
Waiting Areas: Waiting rooms are provided to accommodate patients and their families before appointments or procedures.
Specialized Departments: Medical buildings may house specialized departments like radiology, pathology, surgery, obstetrics, and more, depending on the scope of services offered.
Operating Theaters: Hospitals and surgical centers often have operating rooms equipped for various surgical procedures.
Diagnostic Facilities: Medical buildings can include diagnostic facilities for imaging (X-rays, MRIs, CT scans) and laboratory testing.
Treatment Rooms: These rooms are used for administering treatments such as injections, infusions, and minor medical procedures.
Patient Rooms: In hospitals, patient rooms are designed to provide comfortable accommodations for patients during their stay.
Emergency Services: Hospitals typically include emergency departments equipped to handle urgent medical situations.
Reception and Administrative Areas: Reception desks and administrative offices manage patient registration, scheduling, and medical records.
Healthcare Professionals’ Workspaces: Medical buildings provide spaces for doctors, nurses, and other medical staff to carry out their duties, including offices, meeting rooms, and break areas.
Medical Equipment and Technology: These buildings are equipped with a wide range of medical equipment, including examination tables, imaging machines, surgical tools, and patient monitoring systems.
Infection Control Measures: Medical buildings follow strict hygiene and infection control protocols to ensure patient safety.
Accessibility: Medical buildings are designed to be accessible to individuals with disabilities, with features like ramps, elevators, and accessible restrooms.
Privacy and Confidentiality: Healthcare settings prioritize patient privacy and confidentiality through soundproof walls, secure data storage, and private consultation areas.
Types of Medical Buildings: These include:
- Hospitals: Comprehensive medical facilities that provide a wide range of services, including emergency care, surgeries, and specialized treatments.
- Clinics: Smaller healthcare facilities that offer outpatient care and medical consultations.
- Medical Offices: Private practices where doctors and healthcare professionals see patients for appointments and treatments.
- Specialty Centers: Buildings dedicated to specific medical specialties like cardiology, orthopedics, oncology, and more.
Medical buildings play a critical role in delivering essential healthcare services, promoting well-being, and saving lives. Their design and layout are carefully planned to accommodate medical workflows, patient comfort, and the latest advances in medical technology.
Example of Medical Buildings
Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
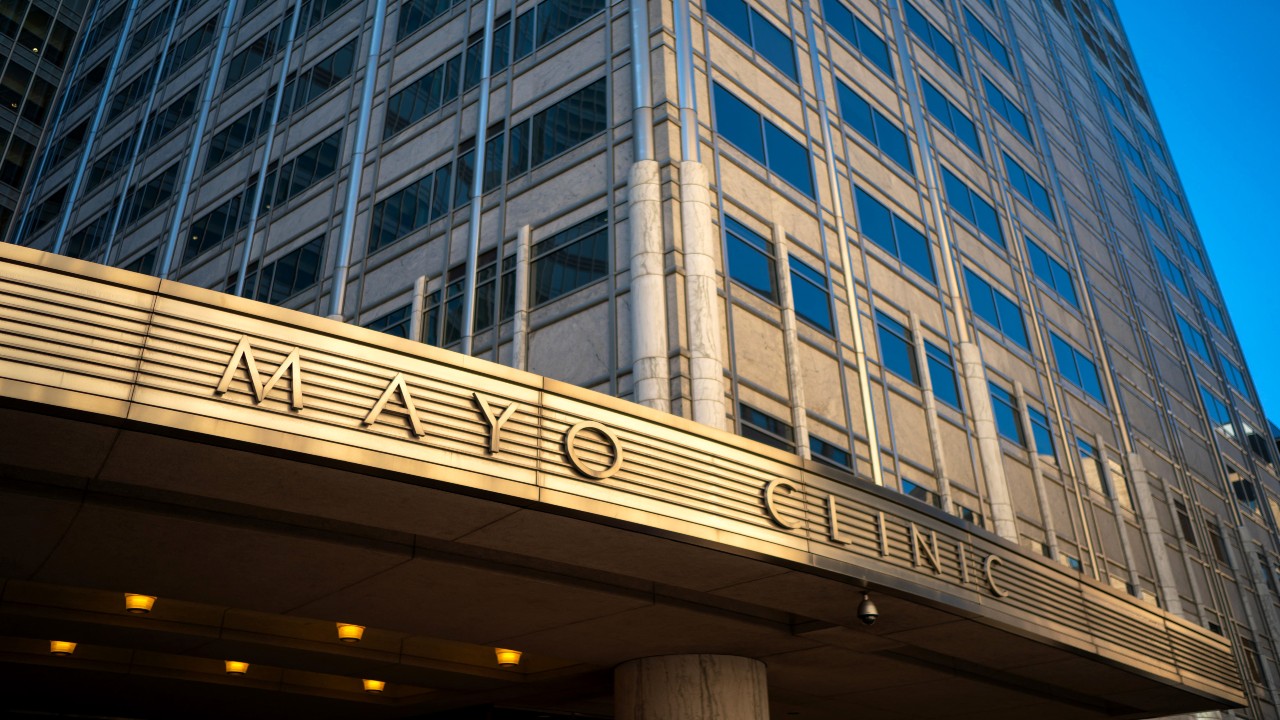

The Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, is a renowned medical complex that encompasses various medical buildings and facilities. It stands as a model of excellence in healthcare and medical research, offering comprehensive care to patients from around the world.
Educational Buildings
Educational buildings are Commercial Building structures designed to facilitate learning, teaching, and academic activities. These Commercial Building are integral to the education system and provide spaces for students, teachers, and staff to engage in a variety of educational endeavors. Educational buildings encompass a wide range of institutions, from schools and colleges to universities and research centers.
Key features of educational buildings:
Classrooms: Educational buildings are equipped with classrooms where teachers conduct lessons, lectures, and interactive discussions with students.
Lecture Halls and Auditoriums: Larger spaces for lectures, presentations, seminars, and public talks are often present in universities and colleges.
Laboratories: Science and research-oriented educational buildings house laboratories for hands-on experiments and practical learning in subjects like biology, chemistry, physics, and engineering.
Libraries: Libraries provide resources, research materials, study spaces, and quiet areas for students to conduct independent study and research.
Common Areas: Educational buildings may include common areas, lounges, and cafeterias for students to socialize and relax.
Administrative Offices: These offices handle enrollment, scheduling, student services, and administrative functions related to the institution.
Computer Labs: Equipped with computers and technology for computer-based learning and training.
Arts and Performance Spaces: Educational buildings in arts-focused institutions may include spaces for music, theater, dance, and visual arts.
Research Centers: Universities and colleges may have research centers dedicated to specific fields of study, offering advanced facilities for research and innovation.
Student Services: Educational buildings often house departments that provide student services, including counseling, career guidance, and academic support.
Collaboration Areas: Modern educational buildings often include collaborative spaces where students can work together on projects and assignments.
Sustainable Design: Many educational buildings incorporate sustainable design elements to promote environmental responsibility and energy efficiency.
Specialized Facilities: Some educational buildings have specialized facilities such as gymnasiums, sports fields, performance stages, and studios for specific subjects.
Access to Technology: Educational buildings are equipped with technology infrastructure to support digital learning, including internet access, audiovisual equipment, and smart classrooms.
Safety Measures: Educational buildings implement safety measures such as fire exits, emergency plans, and security protocols.
Types of Educational Buildings: These include:
- Schools: Buildings that provide primary and secondary education to students.
- Colleges and Universities: Institutions of higher education that offer undergraduate and postgraduate degrees.
- Research Centers: Facilities dedicated to advanced research in various academic disciplines.
- Training Centers: Buildings where vocational and specialized training programs are conducted.
Educational buildings are essential for nurturing the next generation of leaders, professionals, and scholars. Their designs prioritize creating conducive learning environments that support academic growth, creativity, and collaboration.
Example of Educational Buildings
Harvard Yard, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA
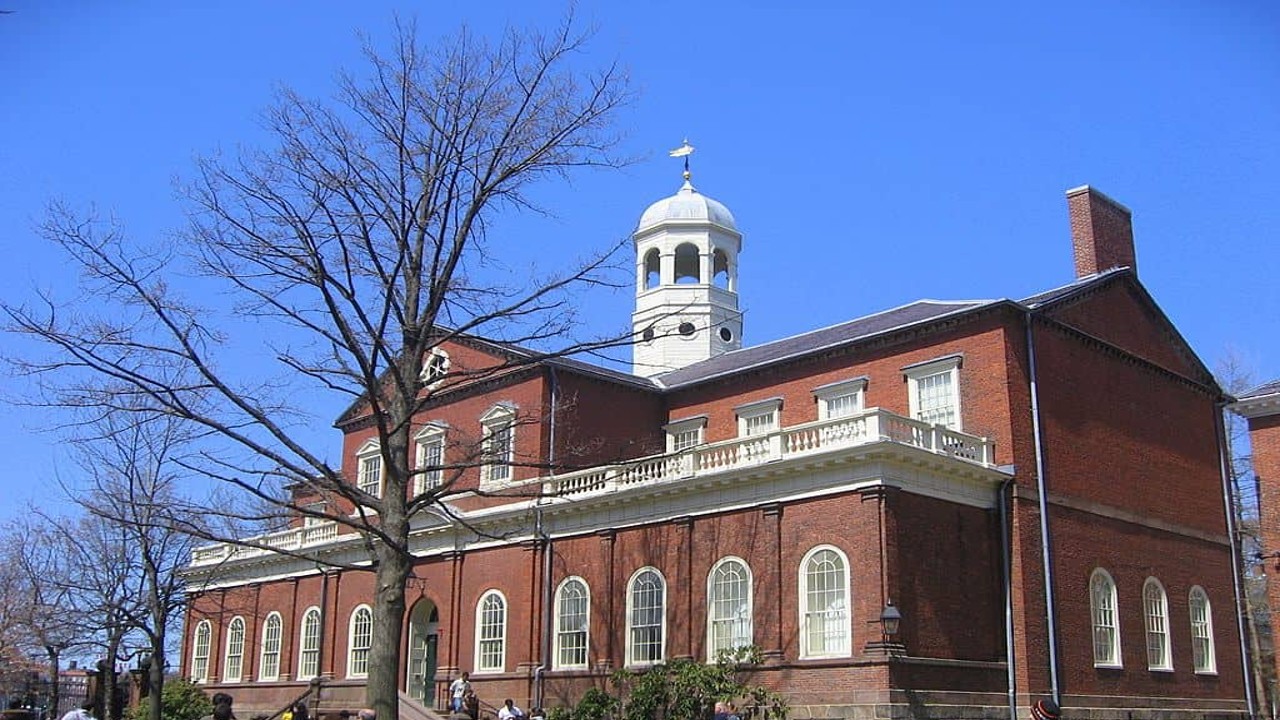

Harvard Yard, located at Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts, is a historic and iconic educational space that houses various educational buildings. It represents a legacy of academic excellence and serves as a hub for learning, research, and intellectual exploration.
Recreational Buildings
Recreational buildings are Commercial Building structures designed to provide spaces for leisure, entertainment, and relaxation activities. These Commercial Building are dedicated to fostering recreational pursuits and offering enjoyable experiences for individuals and groups seeking entertainment and recreational opportunities. Recreational buildings encompass a wide range of facilities that cater to various interests and hobbies.
Key features of recreational buildings:
Indoor Sports Facilities: These buildings may include spaces for activities like basketball, volleyball, indoor soccer, and other team sports.
Swimming Pools: Recreational buildings often house swimming pools, including both lap pools for exercise and leisure pools for relaxation.
Gyms and Fitness Centers: These facilities offer exercise equipment, workout spaces, and fitness classes for individuals aiming to stay active.
Sports Courts: Buildings with spaces for activities like tennis, squash, racquetball, and other racquet sports.
Bowling Alleys: Recreational buildings can include bowling alleys for individuals and groups to enjoy bowling games.
Arcades and Game Centers: These buildings offer arcade games, video games, and interactive entertainment options.
Cinemas and Theaters: Facilities with movie screens and auditoriums for watching films, performances, and theatrical productions.
Dance Studios: Recreational buildings may include dance studios for dance classes and social dancing.
Amusement Parks: Complexes with various attractions, rides, and entertainment options for visitors.
Community Centers: These buildings serve as hubs for community activities, events, and gatherings, offering multi-purpose spaces for different recreational pursuits.
Art Studios and Workshops: Buildings that provide spaces for artistic and creative activities such as painting, pottery, and craft workshops.
Game Rooms: Recreational buildings can have spaces with board games, pool tables, and other social games.
Entertainment Venues: These include music venues, concert halls, and performance spaces for live entertainment events.
Cafes and Lounges: Some recreational buildings feature cafes, lounges, and social areas for relaxation and socializing.
Outdoor Recreational Facilities: These may include outdoor sports fields, parks, and playgrounds associated with the recreational building.
Types of Recreational Buildings: These encompass a variety of facilities, such as:
- Sports Centers: Buildings that offer sports facilities and training opportunities.
- Entertainment Complexes: Venues that provide various forms of entertainment like cinemas, arcades, and game centers.
- Fitness Clubs: Buildings focused on health and fitness, often featuring gyms and exercise facilities.
- Amusement Parks: Complexes with rides, attractions, and entertainment options.
Recreational buildings play a significant role in providing individuals and communities with opportunities for relaxation, physical activity, and social interaction. Their designs are tailored to create environments that encourage enjoyment and engagement in recreational pursuits.
Example of Recreational Buildings
Disneyland Castle, Disneyland Park, Anaheim, California, USA
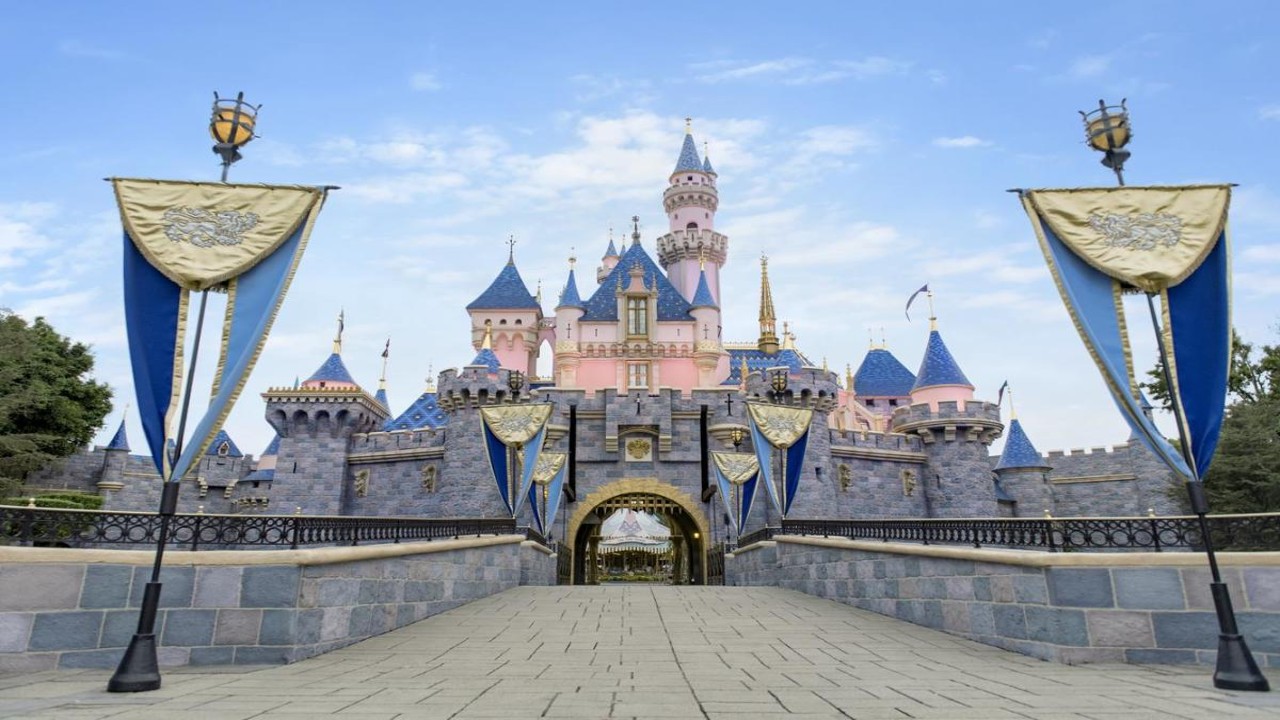

The Disneyland Castle, located at Disneyland Park in Anaheim, California, is a beloved recreational building that embodies the magic and wonder of Disney entertainment. It serves as the centerpiece of the park, enchanting visitors of all ages with its fairy-tale charm.
Conclusion
Commercial buildings form the foundation of modern urban life. Commercial Building create spaces for businesses to thrive, contribute to a city’s aesthetics, and shape its skyline. From towering office complexes to charming local shops, each type of commercial building plays a unique role in shaping the way we live, work, and interact.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the key considerations when designing a retail building?
When designing a retail building, factors such as foot traffic flow, visibility of storefronts, and interior layout to maximize customer engagement are crucial.
How do mixed-use developments benefit communities?
Mixed-use developments promote a sense of community by providing residents with easy access to essential services, entertainment, and living spaces within close proximity.
Are there any eco-friendly features common to modern commercial buildings?
Yes, many modern commercial buildings incorporate energy-efficient systems, sustainable materials, and green technologies to reduce their environmental footprint.
What makes healthcare buildings different from other commercial structures?
Healthcare buildings are designed to accommodate advanced medical equipment, ensure patient comfort, and provide spaces for medical professionals to deliver care.
Can you provide an example of a historic industrial building?
The Ford Piquette Avenue Plant in Detroit, Michigan, is a historic industrial building where the first Model T automobile was produced – Commercial Building