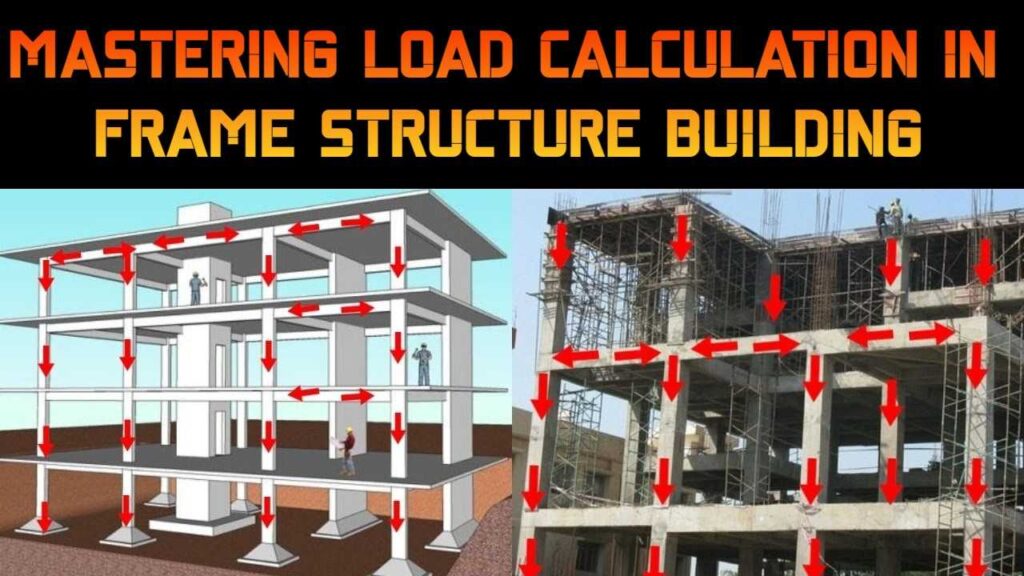
A Foundation in building construction refers to the structural component that supports and distributes the weight of a building or structure to the ground below. It serves as the base upon which the entire building rests, providing stability, strength, and durability.
The main purpose of a foundation is to transmit loads from the building to the soil or rock underneath it in a way that minimises settlement, tilting, and collapse. In particular when dealing with diverse external pressures like gravity, wind, and seismic activity, it is essential for maintaining the building’s structural integrity.
Depending on the exact design needs and site circumstances, foundations are often built with materials like concrete, masonry, or steel. The selection of a foundation type is influenced by a number of variables, including the building’s size and type, groundwater conditions, bedrock depth, and soil’s ability to support weight.
There are different types of foundations commonly used in building construction, including strip foundations, raft foundations, pile foundations, and caisson foundations. Each type has its unique characteristics and applications, allowing builders to adapt to various soil conditions, structural designs, and project requirements.
Types of Foundation in Building Construction
>> Shallow Foundations
- Strip Foundations
- Pad Foundations
- Raft Foundations
>> Deep Foundations
- Pile Foundations
- End-Bearing Piles
- Friction Piles
- Composite Piles
- Pier Foundations
>> Special Foundations
- Raft Mat Foundations
- Caisson Foundations
Shallow Foundations
When the soil close to the surface provides enough bearing ability to sustain the weight of the building, shallow foundations are frequently employed. They are distinguished by their modest depth below the surface of the earth.

Also Read: Top 250 Civil Engineering Interview QnA : PDF Download
Also Read: How To Make BBS Of Pile Foundation
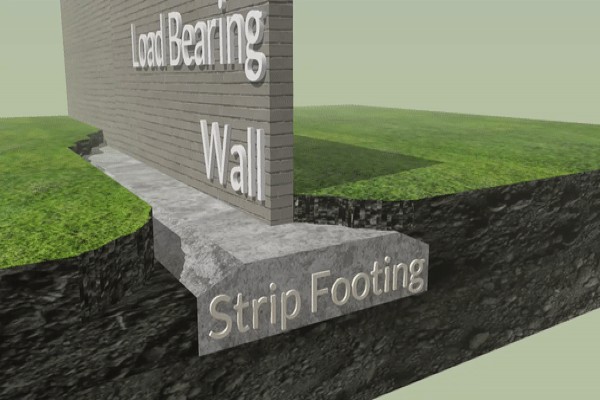
1. Strip Foundations
The load-bearing walls or closely spaced columns are supported by continuous horizontal strips of reinforced concrete, sometimes referred to as spread footings. To reduce settlement and stop differential movement, they spread the load across a broader region.

Benefits of Strip Foundations
- Even Load Distribution: The capacity of strip foundations to equally distribute the load across a larger area is one of its main advantages. This ensures the structural integrity of the structure by preventing excessive settlement and reducing the danger of unequal settlement.
- Cost-effectiveness: Comparing strip foundations to other forms of foundations, they are frequently more affordable. They might reduce the overall cost of the construction project since they need less excavation and material utilisation.
- Versatility: Strip foundations are adaptable to different ground conditions and are multifunctional. They may be made to handle various soil types, enabling building in a variety of settings.
- Stability: Strip foundations offer exceptional stability since they give the building a sturdy base. They reduce the possibility of uneven settling, which can result in structural damage and jeopardise the building’s safety.
Applications of Strip Foundations
- Residential Buildings: In residential construction, strip foundations are frequently employed, especially for low-rise structures. They may support load-bearing walls and uniformly distribute the structure’s weight to the ground.
- Small-Scale Commercial Projects: Strip foundations are also a good choice for modest-sized commercial structures like offices, small warehouses, or retail establishments. They are the perfect option for these kinds of constructions because of their affordability and adaptability.
- Load-Bearing Walls: In particular, strip foundations are advantageous for structures with load-bearing walls. They provide the general stability of the building by serving as a solid foundation for these walls.
- Uniformly Distributed Loads: Strip foundations are advantageous for buildings with consistently distributed loads, such as some industrial structures or storage facilities. The continuous strip of the foundation helps spread out the structure’s weight equally, lowering the possibility of localised settling.
It’s crucial to remember that the applicability of strip foundations depends on a variety of elements, including the soil composition, structural layout, and regional building codes. To guarantee correct design, construction, and adherence to applicable codes, speaking with a trained engineer or foundation specialist is essential.
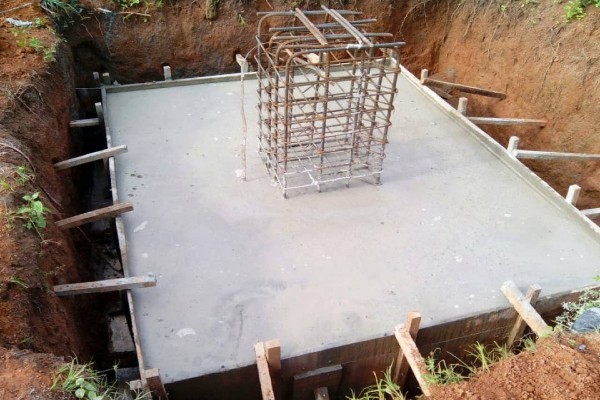
2. Pad Foundations
Individual columns or point loads are supported by pad foundations, which are standalone footings. They are made to transport weight to the earth directly, not to exert much strain on nearby footings. Structures with large concentrated loads frequently employ pad foundations.

Benefits of Pad Foundations
- Simplicity and Cost-effectiveness: Pad foundations are a practical option because of how easy they are to design and build. They may be less expensive since they involve less labour and material than other foundation types.
- Versatility: Pad foundations may be constructed to sustain a range of loads, making them flexible in their purposes. They are able to withstand loads in both the vertical and horizontal axes, stabilising different structural elements.
- Reduced Ground Movement: Ground movement and differential settlement are minimised because to the focused load transmission of pad foundations. This is particularly advantageous in places with diverse soil properties, where differential settling could lead to structural problems.
- Flexibility in Design: To meet the individual needs of the building and the underlying soil conditions, pad foundations can be created in a variety of forms and sizes. This enables modification and adaption to different project requirements.
Applications of Pad Foundations
- Residential Construction: Pad foundations are frequently utilised in residential construction, especially for modest or single-story structures. They guarantee the structural integrity of the home by offering solid support for individual columns or piers.
- Industrial and Commercial Structures: In industrial and commercial structures that need individual column supports, pad foundations are used. They are appropriate for buildings like factories, warehouses, and shopping centres.
- Temporary Structures: Additionally, temporary constructions like construction site offices, modular buildings, or movable cabins employ pad foundations. They are perfect for temporary installations that need rapid and effective foundation solutions because to their simplicity and convenience of building.
- Equipment and Machinery Foundations: Pad foundations are used to support large pieces of machinery, heavy equipment, or standalone units. They offer a solid foundation and aid in distributing the weight, preventing significant settlement or movement.
It is significant to remember that the applicability of pad foundations relies on a number of variables, including the soil conditions, structural loads, and regional building codes. To guarantee correct design and construction, speaking with a certified structural engineer or foundation specialist is advised.
3. Raft Foundations
Raft foundations, also known as mat foundations, are substantial slabs that completely enclose the ground underneath a structure. To ease the strain on the underlying soil, they disperse the load across a wider region. Raft foundations are appropriate for structures built on brittle or uneven soil.
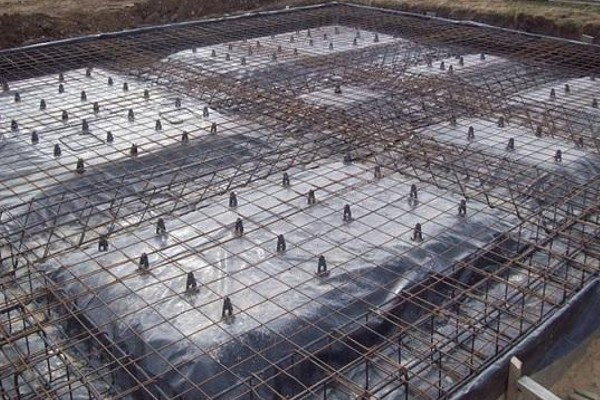

Benefits of Raft Foundations
- Uniform Settlement: Raft foundations are made to minimise differential settling, guaranteeing uniform settlement over the whole building. This aids in preventing structural harm from differential settling, such as wall or floor fissures.
- Stability: Raft foundations provide good stability because to their substantial footprint. They give the building a sturdy foundation by dispersing the weight across a large area, lowering the possibility of foundation failure.
- Versatility in Soil Conditions: Raft foundations may be used in a variety of soil types, even those with low load-bearing capability. In order to make up for poor or unstable soil conditions, they can transmit the weight to deeper, more stable soil layers.
- Reduced Construction Time: Raft foundations can speed up building, particularly in locations requiring a lot of excavation. They eliminate the need for individual footings since they cover the whole ground surface, streamlining and speeding up the building process.
Applications of Raft Foundations
- High-Rise Buildings: Raft foundations are frequently employed in high-rise structures where heavy weights are present. They work effectively for tall buildings that generate high lateral and vertical stresses because of their capacity to disperse the load across a wider region.
- Industrial Structures: Raft foundations are often used in industrial structures, such as factories or warehouses, where there is a presence of heavy gear and equipment. They offer a solid foundation on which these constructions can rest, distributing the weights evenly.
- Areas with Variable Soil Conditions: Raft foundations provide a dependable option in places with changeable soil conditions, such as those with expansive clay or loose fill. They offer steady support for the building and can adjust to the various soil properties.
- Construction on Soft Ground: Raft foundations are particularly helpful for building on soft or compressible ground, such as reclaimed land or coastal locations. They assist in spreading out the load across a bigger area, reducing the chance of settling, and maintaining the stability of the building.
It’s crucial to remember that the development and use of raft foundations call for careful consideration of elements including structural design, soil analysis, and regional building codes. To guarantee that the design and construction of raft foundations are done properly, consulting with a structural engineer who is trained is vital.
Also Read: Foundation Bolts: Types, Application, and Installation Process Explained
Deep Foundations
When the earth at the surface cannot support the weight of the building, deep foundations are used. These foundations go further below the surface in order to transmit the weight to a layer of rock or soil that can support it.
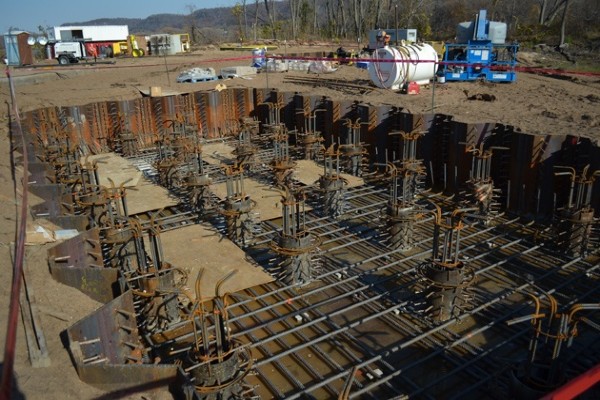

1. Pile Foundations
Long, thin structural components known as pile foundations can be composed of steel, concrete, or wood. To distribute the weight of the building by friction or end-bearing, they are pushed or drilled into the ground.
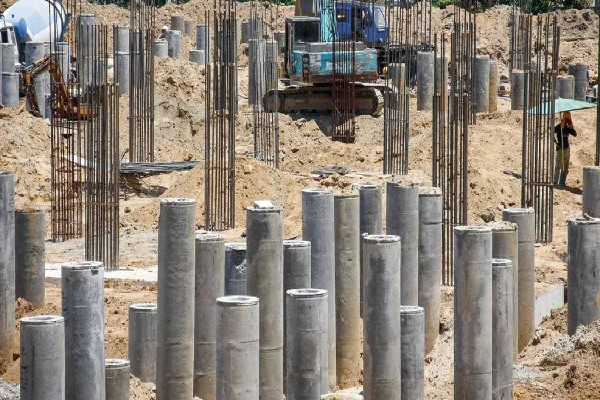

– End-Bearing Piles
End-bearing piles are made to transfer the weight to a solid, load-bearing stratum of rock or soil. They rely on the underlying layer’s resistance to support the structural load.
– Friction Piles
The frictional resistance along the sidewalls of the pile shaft gives friction piles their capacity for bearing weight. They work well in soils that have enough lateral support and cohesiveness.
– Composite Piles
End-bearing and friction pile qualities are combined in composite piles. To offer stability and support, they combine friction and end bearing.
Benefits of Pile Foundations
- Load-Bearing Capacity: Pile foundations are made to support enormous vertical loads and disperse them across deeper, more capable soil or rock layers. As a result, they can sustain heavy structures like high-rise buildings or bridges.
- Suitability for Challenging Soil Conditions: Pile foundations are extremely adaptable and may be utilised in a variety of soil types, including soft, loose, or weak soils, making them suitable for challenging soil conditions. They can avoid using insufficient or inappropriate soil and provide the construction a strong foundation by digging down to deeper, more sturdy layers.
- Improved Stability and Resistance: Pile foundations give good stability and resistance to settlement, which improves stability and resistance. The piles’ deep embedment provide lateral support and aids in their ability to endure forces caused by wind, earthquakes, or other dynamic stresses.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Pile foundations, as opposed to other forms of foundations, cause the least amount of disruption to the environment. They are appropriate for environmentally sensitive places since they need minimal excavation and may be placed without causing significant site disruption.
Applications of Pile Foundations
- High-Rise Buildings: Pile foundations are frequently employed in the construction of high-rise structures. Because of its ability to support vertical loads, piles can withstand lateral stresses and carry the weight of towering structures.
- Bridges and Overpasses: Pile foundations are frequently used in overpasses and bridge building. In addition to provide steady support, they withstand the horizontal stresses and vibrations brought on by driving vehicles.
- Marine Structures: Piers, wharves, and offshore platforms all make considerable use of pile foundations. They offer stability in maritime conditions and can endure the corrosive effects of water.
- Retaining Walls: Pile foundations are another method that is used to build retaining walls. They enable the construction of strong and dependable retaining structures by offering lateral support and preventing soil movement.
- Infrastructure Projects: Pile foundations are used in a variety of infrastructure projects, such as transmission towers, wind turbines, and water treatment facilities. They are useful for supporting large buildings and pieces of machinery because to their stability and load-bearing capabilities.
It’s crucial to remember that both structural engineering and geotechnical engineering knowledge are necessary for the design and execution of pile foundations. There should be significant thought put into the evaluation of factors including pile type, soil analysis, and installation procedures.
Also Read: Design and Construction Of Pile Foundations
2. Pier Foundations
Deep, vertical columns known as pier foundations are used to transmit loads from the superstructure to deeper, more capable soil layers. They are frequently employed in the building of bridges, as well as in regions with high water tables or expansive soil conditions.
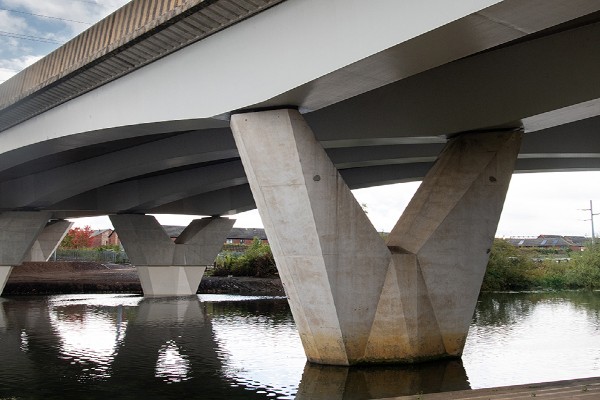

Benefits of Pier Foundations
- Load-Bearing Capacity: Pier foundations are able to support enormous weights because of the way they were built and where they were placed. They give the structure a strong foundation and efficiently transmit the weight to the rock or soil beneath, maintaining stability and averting settlement.
- Versatility in Soil Conditions: Pier foundations may be employed in a range of soil types, including soft or expansive clay. Reaching deeper layers allows them to avoid unstable or inappropriate soil and attach the building to more suitable strata, assuring the integrity of the foundation.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Pier foundations have a lower footprint than other foundation designs, which reduces the amount of environmental disruption that occurs during construction. They are therefore appropriate for work in ecologically sensitive locations.
- Flexibility in Design: Pier foundations provide design flexibility, enabling adaptation based on the unique needs of the structure and site circumstances. To meet varying loading requirements and architectural restrictions, the piers’ size, spacing, and number can be changed.
Applications of Pier Foundations
- Residential Construction: Pier foundations are frequently utilised in residential building, especially in regions with expansive soils or unlevel ground. For homes, cottages, and other low-rise buildings, they offer a solid foundation.
- Bridge Construction: Pier foundations are essential for supporting bridge piers and abutments during building of a bridge. They support the stability and integrity of the bridge by assisting in the weight distribution from the bridge deck and superstructure to the ground.
- Boardwalks and Docks: Pier foundations are ideal for building docks, boardwalks and other waterfront constructions. They enable for safe and dependable access to bodies of water because they provide stability and longevity in maritime conditions.
- Commercial and Industrial Buildings: Pier foundations are furthermore employed in the construction of commercial and industrial structures. For buildings like warehouses, factories, and commercial complexes, they offer a solid and secure foundation that can support the stresses imposed by large machinery and equipment.
- Elevated Structures: Pier foundations are perfect for elevated constructions like elevated homes, viewing platforms, and raised pathways. They enable these buildings to be built atop uneven or difficult terrain by providing the required support and stability.
The design and use of pier foundations necessitate careful consideration of elements including soil analysis, structural design, and load requirements. To guarantee correct design and construction methods, speaking with a skilled structural engineer or geotechnical engineer is vital.
Special Foundations
1. Raft Mat Foundations
Reinforced concrete slabs with a greater span are known as raft mat foundations. They are appropriate for buildings with large weights or those that are built on unfavourable soil.
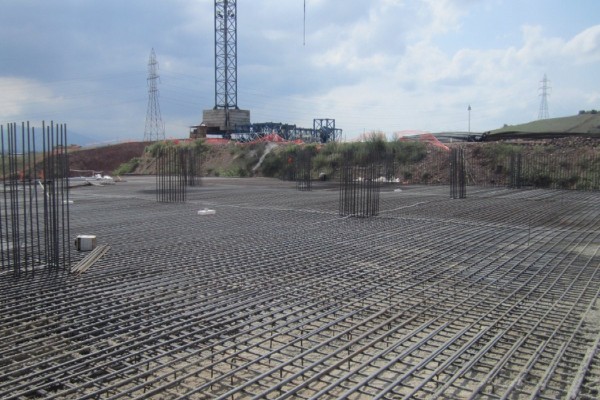

Benefits of Raft Mat Foundations
- Uniform Load Distribution: Raft mat foundations evenly distribute the structure’s weight across a wider area, which lessens the stress on the soil beneath. This keeps the building stable and maintains its integrity while preventing differential settling.
- Reduced Risk of Structural Damage: Raft mat foundations reduce the chance of localised structural damage by dispersing the load across a large region. They create a solid foundation that can endure ground heave, settlement, and differential motions, making the foundation system more strong and long-lasting.
- Improved Seismic Performance: Raft mat foundations have the benefit of offering higher seismic performance than other shallow foundation types, which is a benefit. The continuous character of the foundation contributes to the distribution and dissipation of seismic forces, which strengthens the structure’s ability to withstand earthquakes.
- Suitability for Poor Soil Conditions: Raft mat foundations are especially well-suited for locations with poor soil characteristics, such as expanding clay or loose, compressible soil. They can lessen the possible negative impacts of weak or problematic soil by dispersing the load across a broader area, assuring the integrity of the building.
Applications of Raft Mat Foundations
- High-Rise Buildings: Raft mat foundations are frequently employed in the construction of high-rise structures. They are useful for bearing the heavy vertical loads and maintaining the structural integrity of tall structures because they can disperse the weight evenly across a huge area.
- Industrial Structures: Raft mat foundations have a wide range of functions in industrial facilities, including factories, warehouses, and power plants. These buildings frequently bear tremendous loads, thus a solid foundation system is needed to sustain the machinery and equipment.
- Residential Construction: Raft mat foundations are also used in residential building, particularly in regions with difficult soil conditions. They guarantee a secure and level foundation for homes, apartments, and other low-rise residential buildings by serving as a strong basis.
- Sloping Sites: Construction on sloping locations benefits from using raft mat foundations. They can adapt to changes in ground level, making construction simpler and obviating the need for labor-intensive excavation or intricate retaining walls.
- Seismic Zones: Raft mat foundations are frequently employed in seismically active zones. They increase the structure’s resilience and lessen the possibility of structural damage during seismic events due to their capacity to distribute and disperse seismic stresses over the whole foundation area.
It’s crucial to keep in mind that the design and building of raft mat foundations involve careful consideration of elements including soil research, structural analysis, and appropriate reinforcing details. To guarantee the design satisfies the project’s unique needs, consulting with expert structural and geotechnical engineers is crucial.
2. Caisson Foundations
Watertight retaining structures called caisson foundations are built underwater, then they are pumped dry. They are often employed in the development of dams, bridges, and other maritime infrastructure.
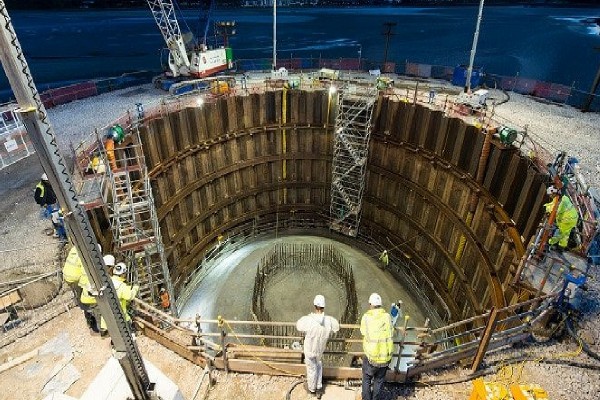

Benefits of Caisson Foundations
- High Load-Bearing Capacity: Caisson foundations are made to support significant vertical loads. They can transfer the load to thicker layers of rock or soil that are more sturdy, assuring the stability and security of the building.
- Versatility in Challenging Soil Conditions: Caisson foundations are adaptable in difficult soil situations, including soft soils, loose sands, and regions with high groundwater levels. They offer a dependable foundation solution and may be utilised in cohesive soils, non-cohesive soils, and even in locations with a high water table.
- Resistance to Lateral Loads: Caisson foundations provide good resistance to lateral loads, including those brought on by wind and seismic pressures. They are stable and don’t move or shift about too much because to their cylindric form and deep embedment.
- Ability to Reach Greater Depths: Compared to other shallow foundation types, caisson foundations have the benefit of being able to reach deeper depths. They are therefore perfect for undertakings requiring deeper foundations, such as large constructions, bridges, and buildings on expanding or unstable soils.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Compared to other foundation types, caisson foundations need less excavation and disturb less land. This lessens the negative effects of building on the surrounding environment, making them appropriate for environmentally sensitive places.
Applications of Caisson Foundations
- High-Rise Buildings: Caisson foundations are frequently employed in the construction of high-rise structures. They are perfect for tall constructions that need robust and dependable foundations due to their capacity to support enormous loads and withstand lateral stresses.
- Bridges and Overpasses: Caisson foundations are frequently used in the building of bridges and overpasses. They provide the safe transmission of loads and withstand the dynamic pressures produced by moving vehicles by offering the bridge piers and abutments the support and stability they require.
- Waterfront Structures: Piers, docks, and wharves are just a few examples of the waterfront structures that are frequently built using caisson foundations. They provide stability and toughness in maritime conditions, resisting the corrosive effects of water and giving these buildings a safe base.
- Industrial and Heavy Equipment Foundations: Caisson foundations are appropriate for sustaining such machinery and large industrial equipment. They can support the heavy weights put on them by machinery like giant cranes, turbines, or storage tanks, giving industrial structures a solid foundation.
- Transportation Infrastructure: Highways, tunnels, and rail networks are just a few examples of the transportation infrastructure projects that use caisson foundations. They sustain the enormous weights and withstand the stresses produced by traffic operations, ensuring the stability and lifespan of these buildings.
It’s important to remember that caisson foundation design and construction call for knowledge of both geotechnical and structural engineering. To guarantee the appropriate operation and performance of the foundation system, factors such soil analysis, drilling procedures, reinforcing details, and concrete mix design must be properly taken into account.
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing the proper foundation is essential for a building’s stability and longevity. For building projects to be effective, it is essential to understand the various foundation types and how well they work with various types of soil and structural loads. Choosing the right foundation guarantees the safety and durability of the project, regardless of whether it is a shallow foundation like a strip, pad, or raft, a deep foundation like a pile or pier, or even a specialised foundation like a raft mat or caisson.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
How do I determine the appropriate type of foundation for my building?
The selection of the foundation type depends on factors such as soil conditions, structural loads, and building design. Consulting with a structural engineer is recommended to determine the most suitable foundation for your specific project.
What are the advantages of shallow foundations?
Shallow foundations are cost-effective, easy to construct, and suitable for buildings with light to moderate loads. They are ideal for stable soil conditions near the surface.
When should I consider using deep foundations?
Deep foundations are used when the soil near the surface is unable to support the building’s load. Factors such as weak soil, expansive soil, or high water table necessitate the use of deep foundations.
Are there any environmentally friendly foundation options available?
Yes, certain foundation types, such as pile foundations, have minimal environmental impact as they require less excavation and use fewer construction materials compared to other types of foundations.
Can I change the foundation type during a building’s construction?
While it is possible to change the foundation type during construction, it is not recommended due to the potential complications and additional costs involved. It is best to determine the appropriate foundation type before commencing the construction process.