Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Load Transfer Mechanism
- 3 What Is Staggering And Why We Need It ?
- 4 Misconception Regarding Staggering
- 5 The problem associated with Staggering
- 6 Possible solutions
- 7 New Concept of Stagger
- 8 What problems would you encounter if you did this on the site
- 9 Other benefits of Staggering every bar
Introduction
Hello, in this article we will learn some core concepts of civil engineering. As we know that, we use TMT bars in RCC construction. These TMT bars are manufactured in 12-meter standard length due to transportation limitations. But do you ever wonder, how multi-story buildings are constructed using this 12 meter long rebar.
Here comes the concept of Rebar Splicing, where we join two rebars and securely transfer the loads from one bar to another bar. But keep in mind that the rebar joint is a weak location, so we should execute it with great concentration. Otherwise, even a small mistake can cause a big problem.
Now the next question is, where do we provide this rebar joint to RCC members?
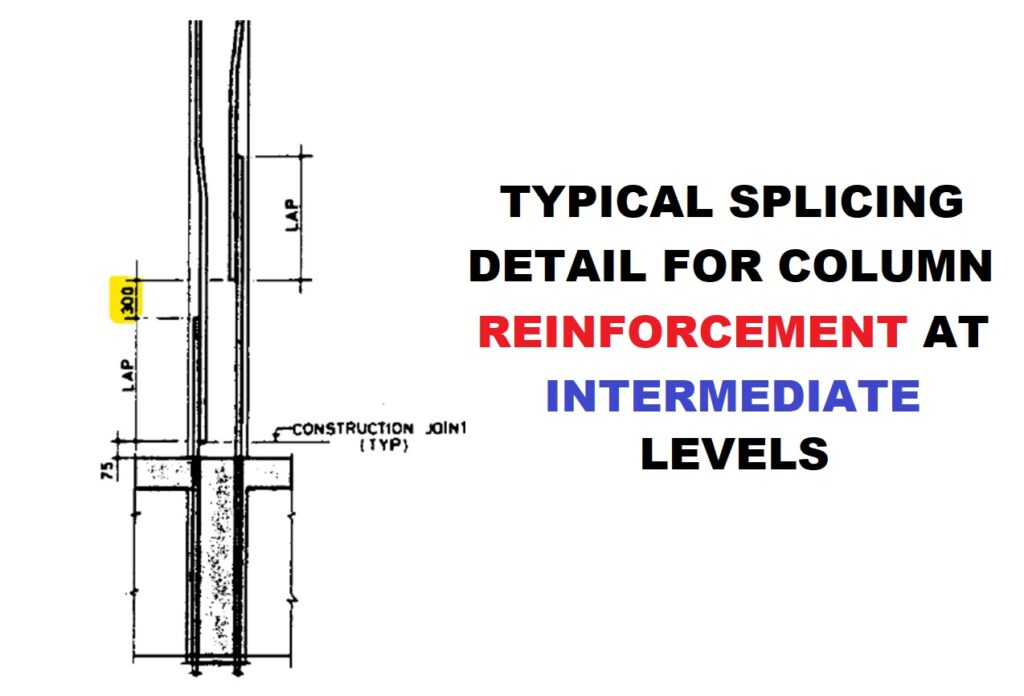
To answer this question, IS code team (Civil Engineers) performed a lot of experiments and analyzed the behavior of RCC members in different loading conditions, different seismic conditions, etc. After this study, IS code divided the RCC column into different zones, which are named zone-A and zone-B as shown below figure.
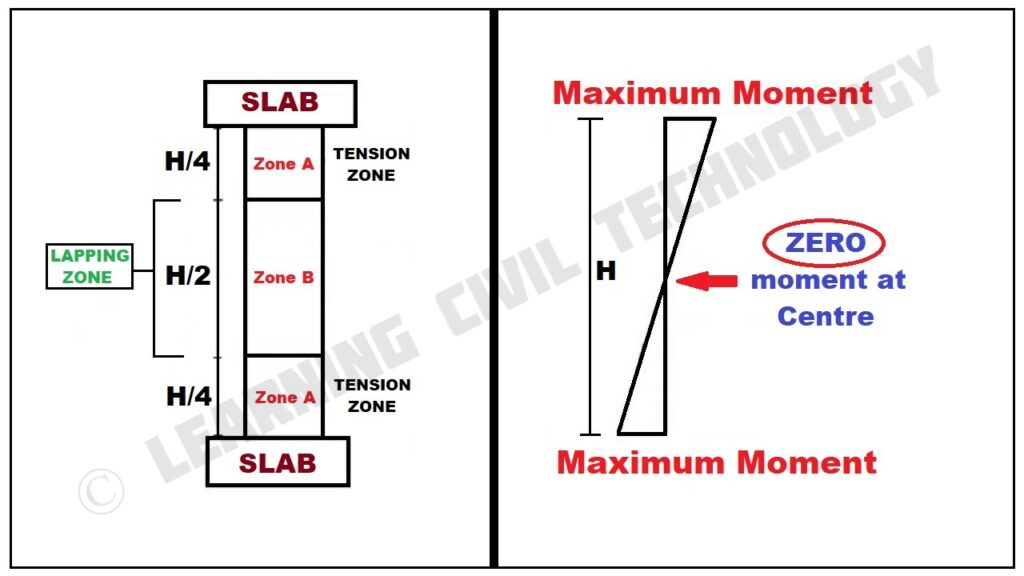
As we can see in the above figure, the bending moment is less in the mid H/2 height of the column as compared to other locations. So rebar splicing is advised in the zone- B of the column i.e. in mid H/2 height of the column.
Methods of Splicing-
- Lapping
- Welding
- Coupler
Load Transfer Mechanism
Now let’s understand, how overlap transfers the load. In the case of lapping, the load transfer through one bar to concrete, then concrete to another bar.
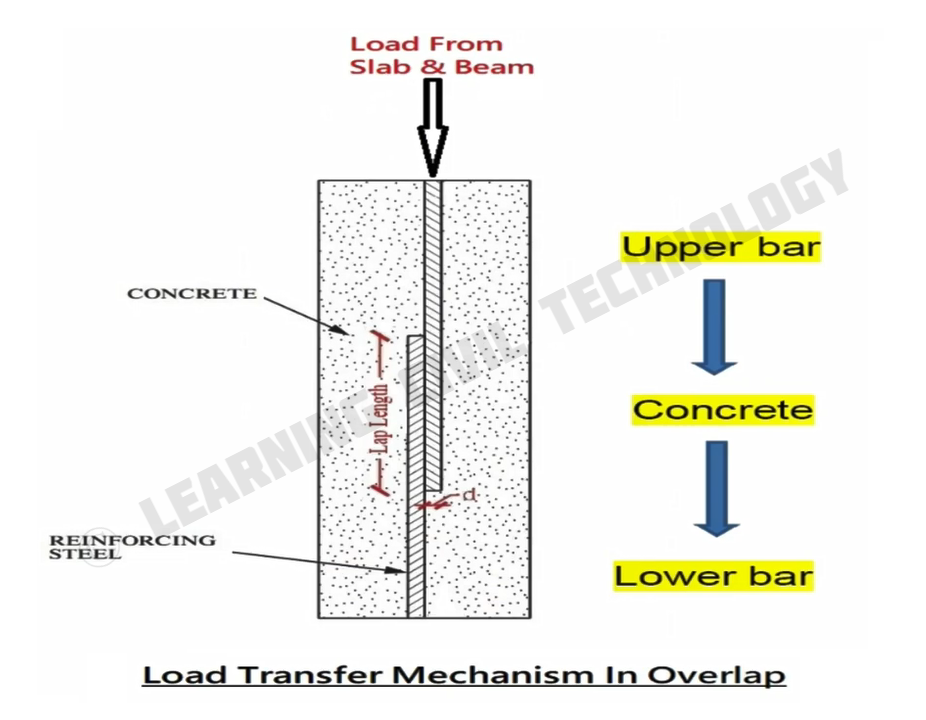
When we overlap two bars, concrete plays an important role in safely transferring the load. But if we provided all overlap at a single location, then concrete will get overstressed and chances of column failure are very high at the overlap location.
To solve this problem, again IS code conducted experiments and came up with the Concept of Staggering.
ALSO READ:
- Top 250 Civil Engineering Interview QnA for Practical Site Interview
- Interview Question asked in Shapoorji
What Is Staggering And Why We Need It ?
As far as we have understood that, rebar joint is a weak point of structure, so it should be away from high-stress locations. That’s why IS code suggested rebar overlap only in Zone B. But if we provided all joints at a single location in zone B, then in case of an earthquake, high-stress concentration will be there, and due to this high stress joint will fail i.e. in case of an earthquake column will collapse suddenly.
So to prevent this sudden failure of the RCC member, IS code makes it mandatory to stagger overlap joints.
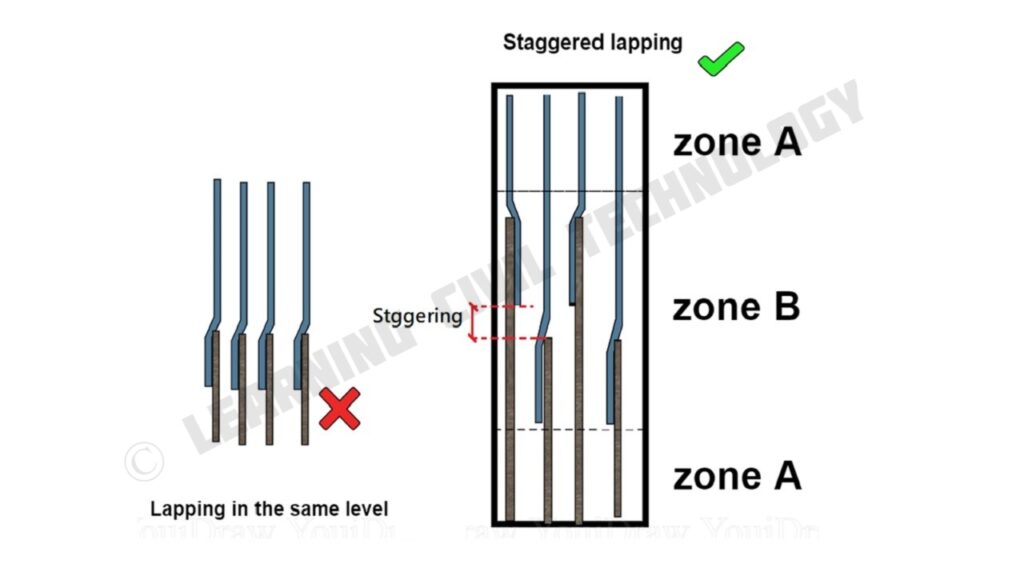
NOW WE HAVE TWO GUIDELINES REGARDING OVERLAP.
1. WE HAVE TO PROVIDE OVERLAP IN ZONE B ONLY,
2. WE HAVE TO STAGGER THE OVERLAP.
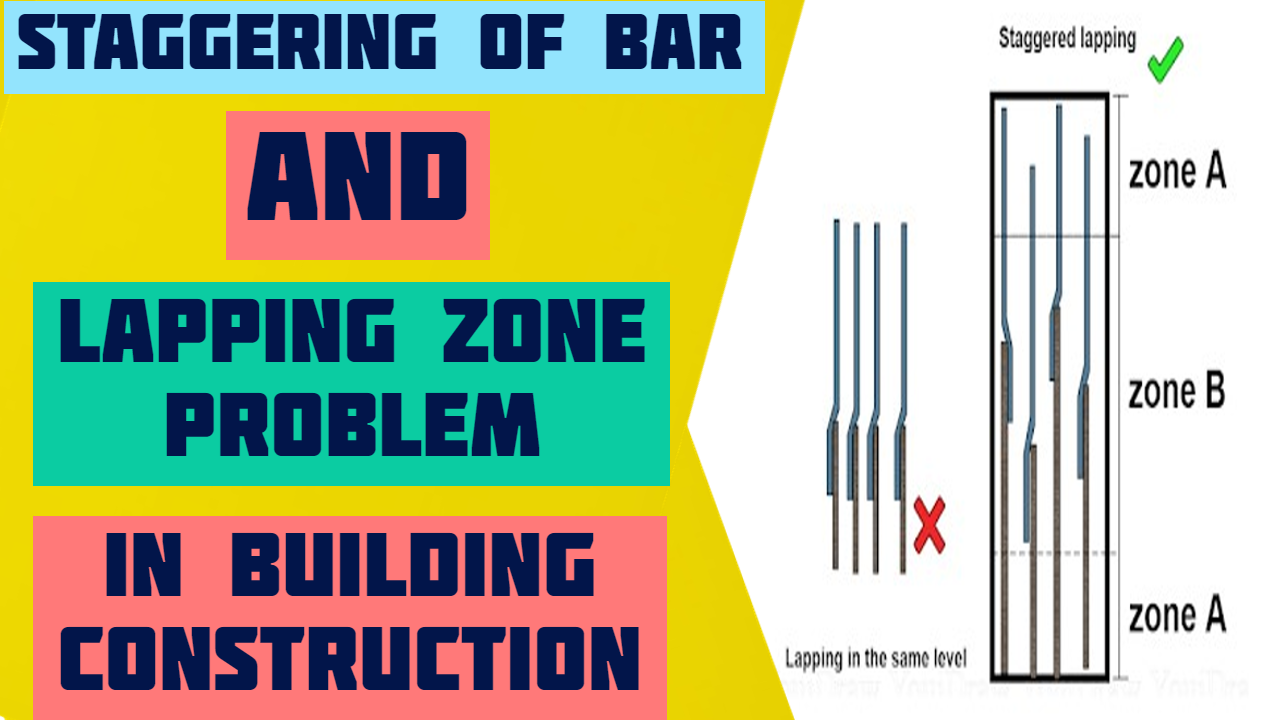
As per SP 34 P.N. 243, the code gives strict guidelines for staggering, as shown in the figure.
Misconception Regarding Staggering
Generally, site engineers in India are not so aware of rebar splicing and its importance. Generally, they measure the 300mm distance between the start of consecutive overlap, which is wrong.
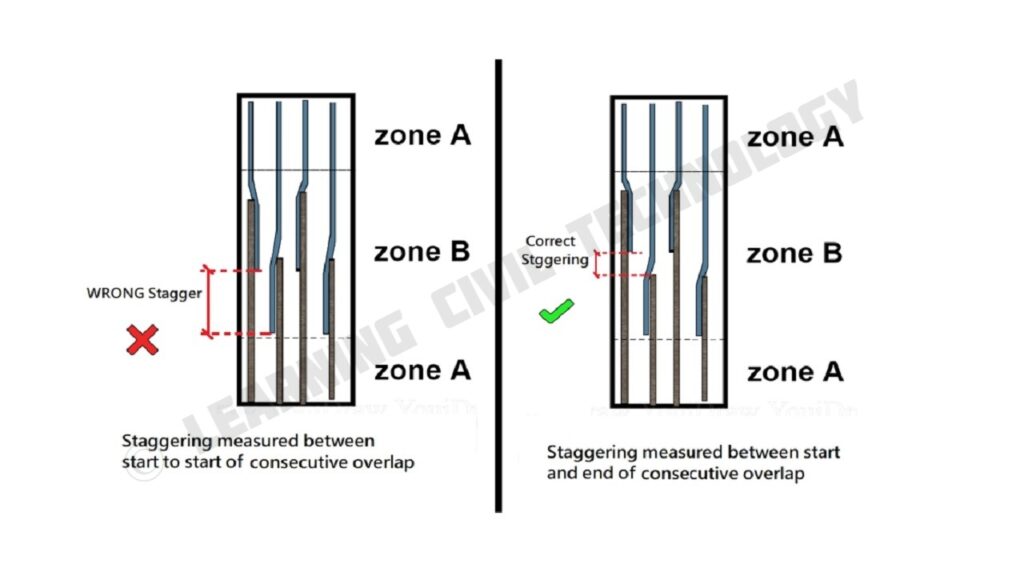
Note:- Correct staggering is one in which there is a clear space of 300mm between the start and end of two consecutive overlaps.
So, we have understood what is Staggering. Now the next question is, how much space between overlap is needed to call any overlap staggered overlap.
As per IS 456 (Cl 26.2.5.1. b) Lap splices shall be considered staggered if the center-to-center distance of the splices is not less than 1.3 times the lap length calculated.
ALSO READ:
- Calculate Gas Pressure Welding Cost for Lapping of Reinforcement Steel Bar for Column, Slab, Beam
- Calculate Coupler Cost for Lapping of Reinforcement Steel Bar for Column, Slab, Beam
The problem associated with Staggering
First of all, if you are overlapping, then you must have to maintain staggering. There are a lot of challenges that site engineer faces during execution.
1. When you are overlapping a higher-diameter bar, it is very difficult to maintain staggering.
2. Joggle slope 1:6 is specified by IS code, but on-site, bar benders can not maintain this particular slope.
Possible solutions
1. Plan to cut the bars in such a way that, only half of the bars overlap on one floor. i.e. cut some of the bars to a longer length and the rest of the bars to the normal length so that half of the bars directly cross the floor and the remaining half overlapped to that floor.
For example,
Floor height = 3m, and rebar diameter is 20mm.
20mm bar length = Two floor height + lap length
= 3m + 3m + 1m (lap)
= 7m
So, if the bar bender installs 7m long rebar, then he can stagger as per IS code guidelines.
But this solution is practically challenging, because bar benders can’t handle such heavy weight. He needs some special equipment (like a crane to support such heavy bars, special scaffolding, etc.) to handle such heavy-weight bars.
Even after so much effort, this 7-meter-long rebar will bend, a lot of times it caused accidents on sites, workers got injuries, and the column gets out of alignment. So bar benders try to avoid longer bars in the column.
2. Use a weld joint instead of an Overlap: Welding impacts the ductility of TMT rebar, so it needs a special type of welding (Flash Butt Weld) that joins the rebar without affecting TMT properties.
3. Use a rebar coupler instead of an Overlap: No need to worry about staggering, as the coupler is a small piece. So 300mm space can be easily maintained.
New Concept of Stagger
IS code suggests that more than 50% of the bar should not be overlapped at a single location (IS: 456 cl. 26.2.5 P.N. 44). This provision of IS code is to safeguard the RCC member from sudden failure.
If we overlap more than 50% bars at a location, then in case of an earthquake high- stress concentration will be at that location, and due to that joint failure chances are very high. But if we reduce the overlapping bars at a single location, then the chances of joint failure reduce significantly.
After understanding the logic behind staggering we have understood that reducing the number of joints at a single location makes the RCC member more strong against earthquakes.
So keeping that thing in view, ConTech brings the idea to stagger every bar by using different length rebar. We are giving flexibility to the user so that he can stagger every bar, i.e. using our concept every bar joint will be at a different location. As all rebar joints are at different locations, chances of failure reduce significantly.
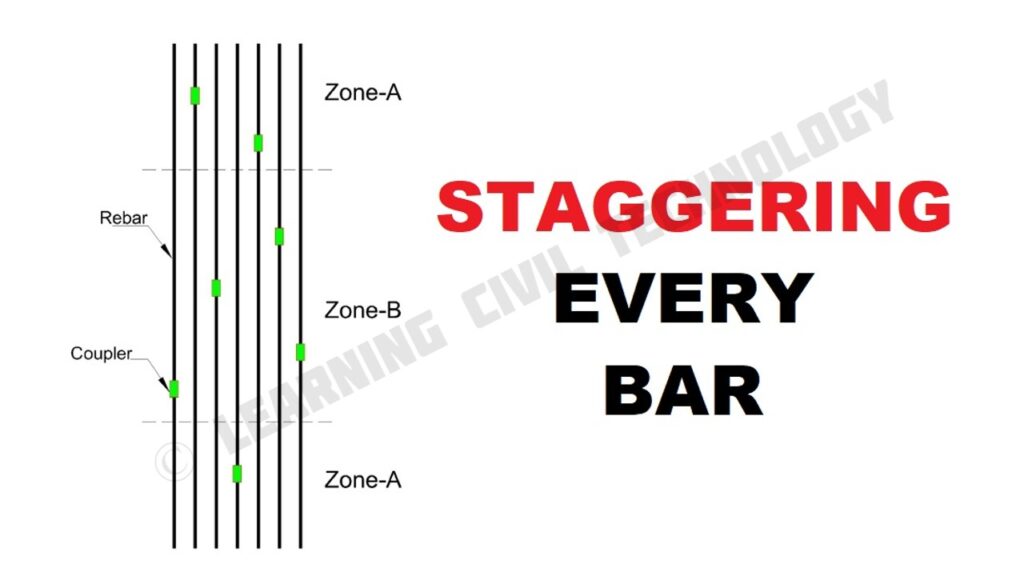
Note:-
1. As per IS 13920, 7.3.2.2 rebar coupler can be used in any zone. so no need to worry about Zone-A or Zone B.
2. Staggering every bar also saves differential weight, which ultimately saves money.
ALSO READ:
- Calculate Cost of Lapping of Reinforcement Steel Bar for Column, Slab, and Beam
- Calculate Number of Labour Required for Manual Excavation with Excel Sheet | CPWD Lecture
What problems would you encounter if you did this on the site
So far we have understood that every bar staggering is a unique concept that makes RCC structure earthquake-resistant. But there are some challenges if bar benders try to execute this concept themselves.
1. The bar bender has to plan the whole process of bar cutting.
At present in India, for column bars bar benders cut the steel in 3 or 4-meter lengths so that a complete 12-meter length can be utilized and no scrap remains. This is a general practice on Indian construction sites. But now to stagger every bar, the bar bender has to cut different lengths for example 3.1m, 3.5m, 4.7m, 3.9m etc, which require a lot of practice. Even then there will be scrap generation.
So to solve this challenge we ConTech provides different length bars so that every bar can be staggered.
2. Bar benders can not cut accurate length bars to stagger every bar.
3. Need a lot of calculations which bar bender can not handle easily.
4. Scrap generation will make every bar stagger more costly.
ConTech at factories, cut different length bars precisely to stagger all bars. This new concept of staggering each bar is only possible through Coupler and staggering each bar makes the structure more strong.
Other benefits of Staggering every bar
ConTech – Technical products based company. We are dedicated to changing the wrong construction practices that negatively impact the environment as well as increase the cost of building.
As we discussed staggering every bar is good for building, but bar benders can’t execute it directly themselves.
ConTech provide ready-to-install threaded rebars of different lengths so that you can use a rebar coupler and stagger every bar.
There are some other hidden benefits of buying a threaded bar from ConTech-
1. Differential weight
Let’s understand differential weight with an example. Take a closer look at the figure below.
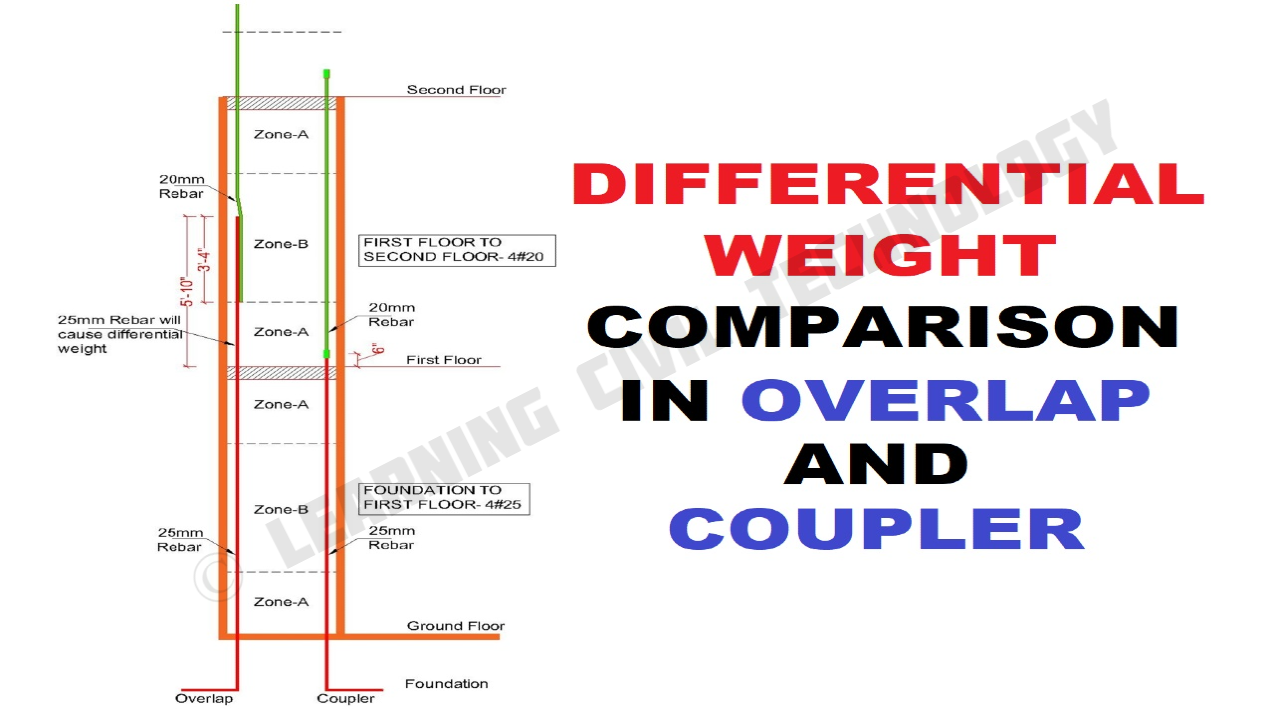
CALCULATION OF DIFFERENTIAL WEIGHT –
4 Nos, 20mm rebar is required for the first floor to the second floor, but due to the overlapping zone we have to provide 4 Nos, 25mm bar for 5′-10″ height.
Weight of 5′-10″ rebar of 25mm = 6.85 kg
Weight of 5′-10″ rebar of 20mm = 4.38 kg
So, Differential Weight of 4 rebar = 4x(6.85-4.38) = 9.88 kg
But in the case of the rebar coupler, the differential weight ≈ 0 kg
Note:- Differential Weights and Overlapping Weights are two separate weights, that can be saved by using a rebar coupler.
2. Cost comparison of overlap v/s coupler free of cost.
Contech offers a free service of Cost comparison (CC) to our customers so that you can visualize the savings amount.
You can take column rebar quantity directly from CC for every floor.
3. On-site color marking on Rebars.
Bar benders install the bars as per current floor requirement, so they install 3 or 4m long bars. a lot of times diameter of the rebar changes when the column enters in next floor. But the bar bender already placed 3 or 4m long bar, which will cause differential weight.
To save this differential weight, we ConTech will facilitate the color marking on site and provide a highlighted drawing. i.e. those bars whose diameter is changing on the next floor we will mark them so that the bar bender will install short-length rebar over the existing rebar. And over the remaining bars, normal-length bars can be installed. So this is how we can save differential weight problem.
Also, the chances of error are minimized by color marking.
If You Want Detailed Knowledge Then Watch My Video On YouTube Channel: Learning Civil Technology. I Am Telling This Because Many Important Points I Have Covered During Making Of Video, So If You Want To Know In Detail Then Watch My Video On YouTube Which is Given Below.
You can also follow me on Instagram, Telegram and Facebook page. Because many small things, which are very important from interview point of view, it is not possible to put here, I put all that on Instagram, Telegram and Facebook page. You can take it from there. You will find the links of all social media below.
INSTAGRAM | TELEGRAM | FACEBOOK PAGE