Concrete is a versatile construction material composed of a mixture of cement, sand, coarse aggregates (such as gravel or crushed stone), and water. It is widely used in the construction industry for various applications, including building foundations, walls, floors, pavements, and structures like bridges and dams.
Contents
Components of Concrete
Here’s a brief overview of the components of concrete:
- Cement: Limestone, clay, shale, and other elements are frequently used to make cement, a fine powder. As a binder, it keeps the concrete mixture together. Portland cement is the kind of cement that is most often used.
- Sand: Sand, commonly referred to as fine aggregate, is a granular substance used in concrete mixes to fill the voids left by the bigger aggregates. It contributes to giving strength and adaptability.
- Coarse Aggregates: Coarse aggregates are bigger particles that add bulk and stability, such as gravel or crushed stone. They add to the strength of the concrete and make up the majority of its volume.
- Water: Adding water to cement causes it to hydrate, a chemical process that hardens the cement and fuses the other elements together. The workability and strength of the concrete are influenced by the water content in the mix.
Fresh concrete is created during construction by mixing the right amounts of cement, sand, coarse particles, and water to create a plastic substance. This mixture may be put into moulds or formwork, where it will eventually cure and solidify, strengthening and becoming more durable. For the concrete to have the appropriate qualities, good curing, and sufficient hydration are crucial.
It’s significant to note that several mixed kinds are available, each with unique ingredients and quantities designed to satisfy certain needs. Ready-mix concrete, self-compacting concrete, high-strength concrete, and others are some examples. The intended application, structural design, ambient circumstances, and required performance characteristics are only a few examples of the variables that influence the choice of concrete mix.
Depending on the required strength, the kind of concrete mix, and the needs of a particular project, the ratio of cement, sand, and aggregate (often referred to as coarse aggregate) in concrete might change. However, I can give you a few standard ratios for various concrete mix types.
- Standard Concrete Mix (1:2:4):
- Cement: 1 part
- Sand: 2 parts
- Aggregate: 4 parts
- Reinforced Concrete Mix (1:1.5:3):
- Cement: 1 part
- Sand: 1.5 parts
- Aggregate: 3 parts
- High-Strength Concrete Mix (1:1:2):
- Cement: 1 part
- Sand: 1 parts
- Aggregate: 2 parts
Please take note that the aforementioned ratios are provided by volume. For precision and consistency, weight measurements are typically used in practice. The precise amounts of cement, sand, and aggregate needed for a given volume will vary depending on each component’s density or unit weight.
The best mix design, as well as the proper proportions and quantities for your particular project, should be determined by consulting a structural engineer or expert, as they may vary depending on factors like the required strength, exposure conditions, and local building codes and standards.
Today in this tutorial I am going to tell you How to calculate Cement, Sand, and Aggregate Quantity in Concrete in very easy steps at Construction Sites. So let’s start.
Calculation: Cement, Sand, And Aggregate Quantity In Concrete
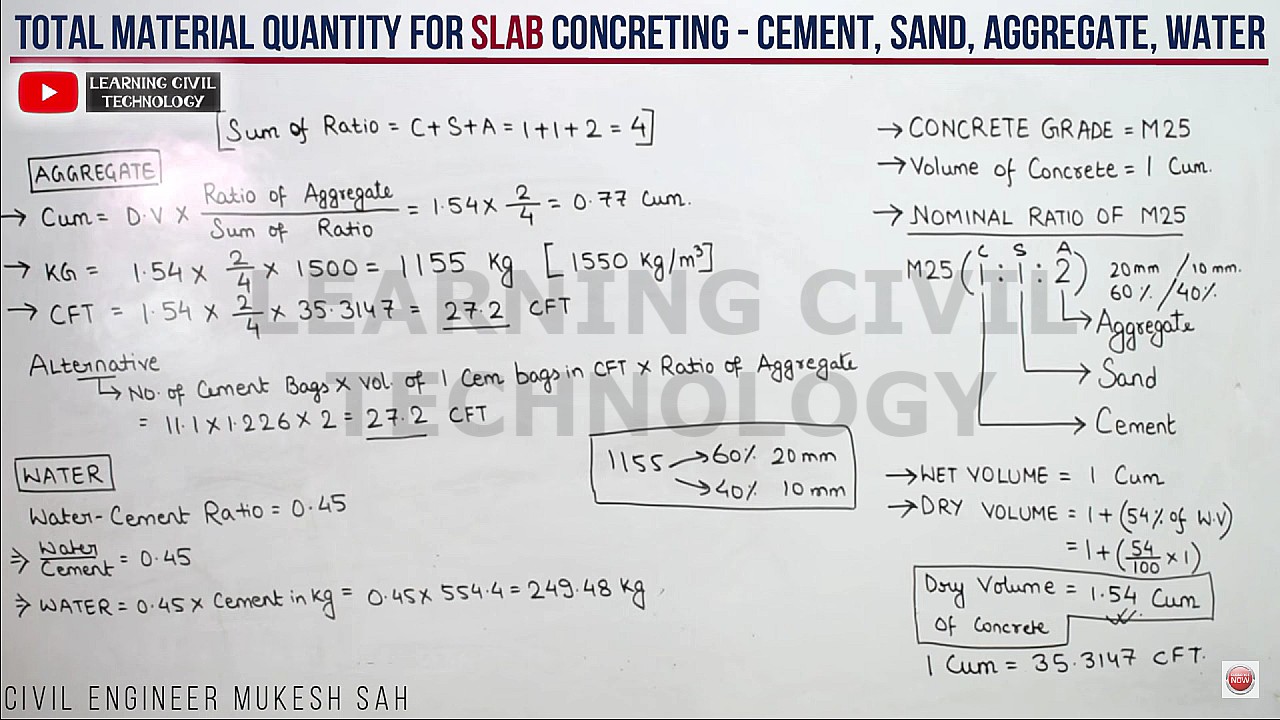
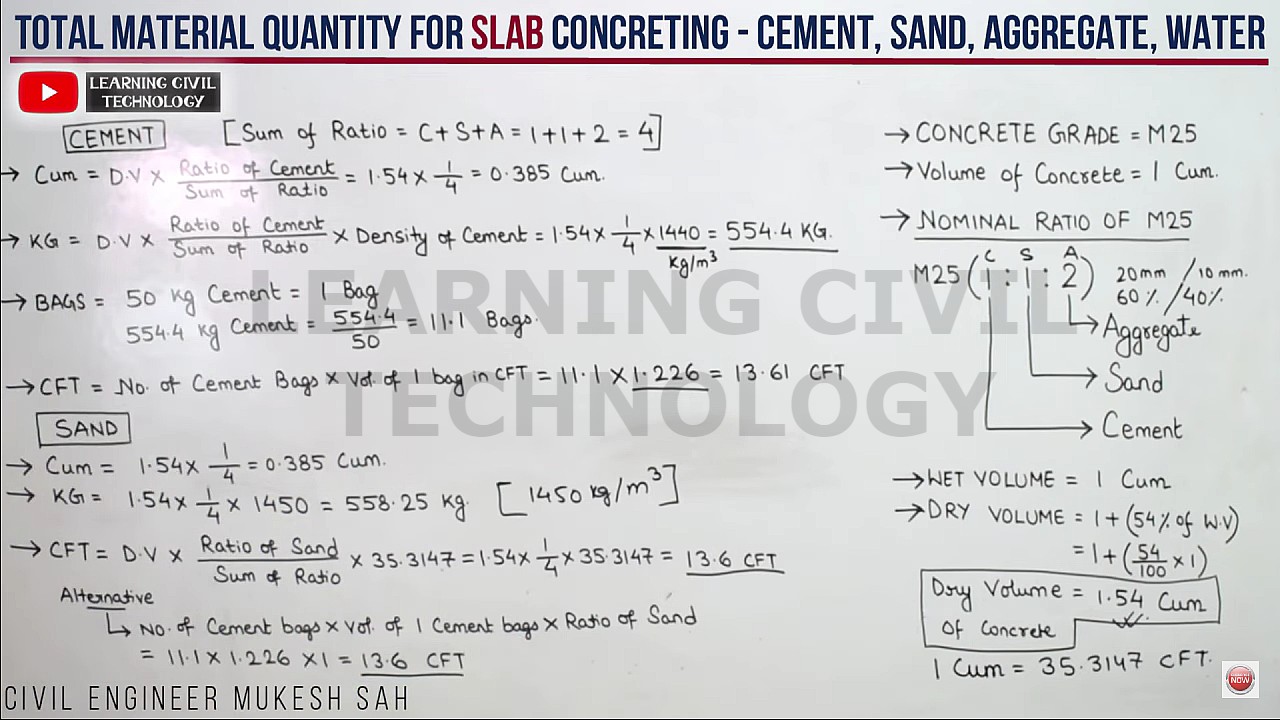
Here I have considered concrete volume (WET) = 1 cubic meter (m³)
Grade of concrete mix = M15 (Cement = 1 : Sand = 2 : Aggregate = 4)
Sum of the ratio of cement, sand & aggregate = 1+2+4 = 7
First, we have to find the Dry Volume of concrete by increasing the Wet Volume by 54 percent.
Dry Volume = Wet Volume x (54% of Wet Volume)
= 1 x (54 x 1 / 100) = 1.54 cubic meter (m³)
Now we have to find the quantity of Cement, Sand & Aggregate. Here I will show you the calculation of quantity in different units like Cubic Meters, KG, Bags, and Cubic Feet.
ALSO READ:
Mix Design Of Concrete As Per IS 10262
Quantity of Cement in Concrete
1) Cubic Meter = Dry Volume x (Ratio of Cement / Sum of Total Ratio)
= 1.54 x (1 / 7) = 0.22 Cubic Meter
2) KG = Dry Volume x (Ratio of Cement / Sum of Total Ratio) x Density of Cement
= 1.54 x (1 / 7) x 1440 = 316.8 KG
3) Bags = We know, 50 KG = 1 Bag of Cement
So, 316.8 KG = 316.8 / 50 = 6.336 Bags of Cement
4) Cubic Feet = If we multiply the Number of Cement bags by 1.226, we get the value in Cubic Feet i.e. 6.336 x 1.226 = 7.77 Cubic Feet
Quantity of Sand in Concrete
1) Cubic Meter = Dry Volume x (Ratio of Sand / Sum of Total Ratio)
= 1.54 x (2 / 7) = 0.44 Cubic Meter
2) KG = Dry Volume x (Ratio of Sand / Sum of Total Ratio) x Density of Sand
= 1.54 x (2 / 7) x 1450 = 638 KG
[Density of Sand varies between 1450 – 1500 KG per Cubic Meter]
3) Cubic Feet = Dry Volume x (Ratio of Sand / Sum of Total Ratio) x 35.3147
= 1.54 x (2 / 7) x 35.3147 = 15.54 Cubic Feet
[NOTE : 1 Cubic Meter = 35.3147 Cubic Feet]
No. of Cement Bags x Value of one bag of cement in Cubic Feet x Ratio of Sand
= 6.336 x 1.226 x 2 = 15.54 Cubic Feet
Quantity of Aggregate in Aggregate
1) Cubic Meter = Dry Volume x (Ratio of Aggregate / Sum of Total Ratio)
= 1.54 x (4 / 7) = 0.88 Cubic Meter
2) KG = Dry Volume x (Ratio of Aggregate / Sum of Total Ratio) x Density of Aggregate
= 1.54 x (4 / 7) x 1500 = 1320 KG
[Density of Aggregate varies between 1450 – 1550 KG per Cubic Meter]
3) Cubic Feet = Dry Volume x (Ratio of Aggregate / Sum of Total Ratio) x 35.3147
= 1.54 x (4 / 7) x 35.3147 = 31.07 Cubic Feet
[NOTE : 1 Cubic Meter = 35.3147 Cubic Feet]
ALTERNATIVE: No. of Cement Bags x Value of one bag of cement in Cubic Feet x Ratio of Aggregate
= 6.336 x 1.226 x 4 = 31.07 Cubic Feet
DOWNLOAD NOTES
Below I am uploading my handmade Notes on your request so you can download them. But one thing keep in mind is that this is only handmade Notes.
REFERENCE VIDEO
If you want detailed knowledge, then watch this Reference video on YouTube Channel: Learning Civil Technology. Because many important points have been covered during the making of the video, so Must Watch. The link is given below:
SOURCE: LEARNING CIVIL TECHNOLOGY
You can also follow me on Instagram, Telegram, and Facebook page. Because many small things, which are very important from an interview point of view, it is not possible to put here, I put all that on Instagram, Telegram, and Facebook page. You can take it from there. You will find the links to all social media below.
INSTAGRAM | TELEGRAM | FACEBOOK PAGE
SHARE THIS POST, IF YOU LIKE IT !! THANKS







how much Quantity of water ?
Sir how to download this
How to download this
Thanks…..
thank you , u r doing really good job sir
This comment has been removed by the author.
Thank you soo much sir….
Thank you soo much sir….
Mujhe pta nhi hai
Mujhe pta nhi hai
1.54
can ratio of dry water ratio change in other concret ratio means M25 etc
good work , keep going on it's very helpfull.
sir job ki requirement hai
Thanks sir
sir girder ka bbs bataye please..
sir;M35 ya kisi v design mix k nikalna ho to kse nikalnge
sir, quantity of water?
w/c=.40
then 50*.40=20 ltr per bag of cement