The efficiency of a centrifugal pump is an essential factor to consider when evaluating its performance and energy consumption. Efficiency is a measure of how effectively the pump converts the input power into useful hydraulic energy, which is transferred to the fluid being pumped. Higher efficiency implies that the pump requires less input power to achieve the desired flow rate and head.
Contents
Several factors influence the efficiency of a centrifugal pump:
- Pump Design: The design of the pump, including the impeller, volute or diffuser, and casing, plays a crucial role in determining its efficiency. Well-designed components can minimize hydraulic losses and maximize the conversion of mechanical energy into fluid flow.
- Operating Point: The efficiency of a centrifugal pump varies with its operating point on the pump curve. Operating away from the best efficiency point (BEP) can significantly reduce the pump’s efficiency. It is important to select a pump that matches the required flow rate and head to operate close to the BEP for optimal efficiency.
- Hydraulic Conditions: The pump’s efficiency can be affected by the fluid properties being pumped, such as viscosity and density. Non-ideal fluid conditions, including cavitation (formation of vapor bubbles), can lead to reduced efficiency and potentially damage the pump over time.
- Mechanical Factors: The mechanical condition of the pump, including wear and tear of impeller blades, seals, and bearings, can impact its efficiency. Regular maintenance and proper alignment of pump components are essential to ensure optimal efficiency.
- Motor Efficiency: The overall efficiency of a centrifugal pump system also depends on the efficiency of the motor driving the pump. Using a high-efficiency motor can contribute to overall energy savings.
It is important to note that the efficiency of a centrifugal pump is highest near the BEP and tends to decrease at lower or higher flow rates. Pump manufacturers often provide pump curves that indicate the efficiency at various operating points, allowing users to select the most efficient operating conditions for their specific requirements.
The efficiency of a centrifugal pump is a critical performance parameter that influences its energy consumption. Proper pump selection, regular maintenance, and operating at or near the BEP are key considerations to maximize pump efficiency and minimize energy costs.
The objective of the Experiment:
To determine the efficiency of the centrifugal pump
Theory:
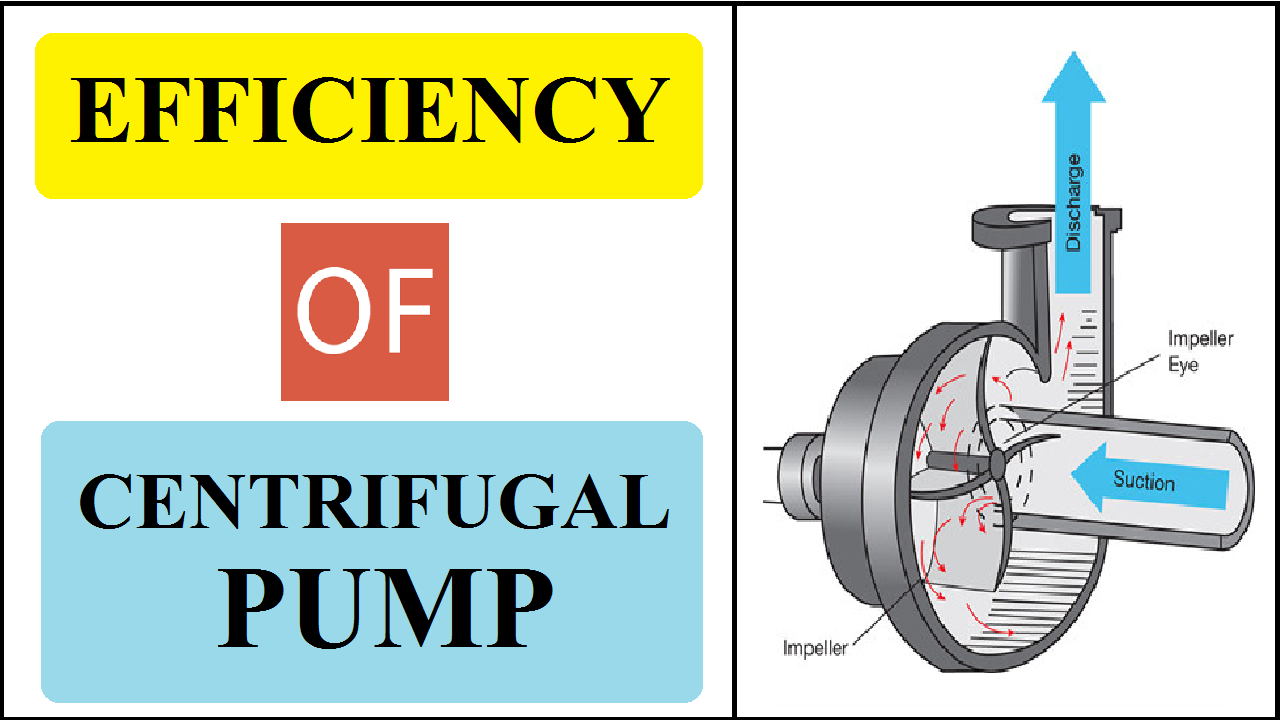
Centrifugal pump is a Roto Dynamic Machine which develops dynamic pressure of liquid by virtue of rotation for pumping of liquid to a higher height. In a centrifugal pump, liquid in the impeller of a pump is made to rotate by an external force, so that it is thrown away from the center of rotation. As the constant supply of liquid is made available at the center, the liquid can be pumped to a higher level.

The unit consists of a centrifugal pump driven by an A.C motor. Input to the motor is measured by energy meter. A measuring tank is provided to measure the discharge. Suction vacuum and discharge pressure are measured by gauges. A gate valve on the discharge pipe varies the head. Thus, the performance of the pump can be estimated at various speeds and heads.
Apparatus Required:
1. Centrifugal pump – Base mounted, Maximum head 20 meters, Maximum discharge 84 litres per minute at 2700 revolution per minute (RPM)
2. Mortar – A.C, 1 HP, 3 phase, Induction motor
3. Measuring tank – 300 mm x 300 mm x 450 mm height, fitted with gauge tube and drain valve
4. Sump tank – 900 mm x 300 mm x 400 mm height
5. Gate valve to control the head
6. Pressure gauge to measure the discharge pressure
7. Vacuum gauge to measure suction vacuum
8. Energy meter to measure input the motor
9. Stopwatch
ALSO READ:
- Calibration of V-Notch Experiment
- Aggregate Impact Value Test as per IS 2386 (Part-IV) 1993
- Aggregate Crushing Value Test
- Water Content of Soil by Oven Drying Method
- Specific Gravity of Cement by Specific Gravity Bottle
- Sp. Gravity & Water Absorption Of Coarse Aggregate
- Sp. Gravity & Water Absorption of Fine Aggregates
Experimental Procedure:
1. Fill up sufficient water in the sump tank.
2. Open the priming cock (fitted on the delivery pipe) and fill up water up to the funnel. Close the cock properly.
3. Shut off the discharge valve.
4. Start the pump. As the discharge valve is closed, no discharge will be observed, but discharge pressure will be indicated. This is called ‘shut off head’ of the pump.
5. Slowly open the discharge valve, so that small discharge is observed.
6. Note down discharge head, suction vacuum, the time required for 10 cm rise in the measuring tank and 10 impulses of energy meter.
7. Note down the observations at different valve openings.
Observations
| SL No. | Discharge Pressure (Pd) (kg/cm2) | Discharge Head (hd) (meter of water) | Suction vacuum (Ps) (mm of Hg) | Suction Head (hs) (meter of water) | Friction Loss Head (hf) (meter of water) | Time for 10 cm rise of water (seconds) | Time for 10 impulses of Energy meter (seconds) |
|
1 | |||||||
|
2 | |||||||
| 3 |
|
Calculations: Efficiency of a Centrifugal Pump
1) Discharge Pressure, (Pd) (kg/cm2)
For water, 10-meter height corresponds to 1 kg/cm2
Therefore, Discharge Head (hd) = Pd x 10 meters of water
2) Suction Head –
Suction Vacuum, (Ps) (mm of Hg)
Therefore, Suction Head (hs) = (Ps/1000) x (13.6 / 1)
where Specific Gravity of Hg = 13.6 and Specific Gravity of water = 1
3) Total Head
ht = hd + hs + hf
where, hf = the assumed head loss due to friction in meter (Say 0.5 meter)
4) Discharge
Let time for 10 cm rise of water in measuring tank be ‘t’ seconds.
Then, Discharge, Q = (0.3 x 0.3 x 0.1 / t) m3/sec
5) Output Power (or Water Power)
WP = [(W x Q x ht ) / 1000] kW
where, W = Specific Weight of water = 9810 Newton per cubic meter, Q = Discharge (meter cube per second), ht = Total Head (metre of water)
6) Electrical Input
Let time required for 10 blinks of energy meter be te – second
Electrical input power, IP = [(10/te) x (3600/1600)] kW
Taking motor efficiency as 60% we have input shaft power,
SP = IP x 0.6
7) Overall Efficiency of pump
ηo = (WP/SP) x 100 %
Precautions:
1. Priming is a must before starting the pump. The pump should never run dry.
2. Use clean water in the sump tank.
3. Use all the controls and switches carefully.
4. Do not disturb the pressure gauge connections.
5. Drain all the water from the sump tank after the experiment is completed.
Social Pins
You can also follow me on Instagram, Telegram and Facebook page. Because many small things, which are very important from interview point of view, it is not possible to put here, I put all that on Instagram, Telegram and Facebook page. You can take it from there. You will find the links of all social media below.
INSTAGRAM | TELEGRAM | FACEBOOK PAGE
SHARE THIS POST, IF YOU LIKE IT !! THANKS






Thank you so much Sir