A dumpy level is a precision optical instrument used in surveying and engineering to establish and measure horizontal lines, as well as to determine relative heights or elevations of different points on the ground. It consists of a telescope mounted on a tripod and a leveling mechanism to ensure accuracy.

Contents
Use of Dumpy Level
A dumpy level is a fundamental surveying instrument that plays a crucial role in various engineering and construction projects. It is primarily designed for leveling and height determination tasks, offering simplicity and accuracy. Let’s delve into the detailed uses and applications of a dumpy level:
Establishing Horizontal Reference Lines
One of the primary uses of a dumpy level is to establish accurate horizontal reference lines on construction sites. This is essential for ensuring that structures like buildings, roads, and bridges are constructed on level ground. The dumpy level helps in maintaining the required levelness for the foundation and other critical components of the project.
Determining Height Differences
Dumpy levels are indispensable for determining height differences between different points on the ground. This is especially important for creating topographic maps, calculating contours, and understanding the shape of the terrain. Surveyors use dumpy levels to measure the vertical distance between a known reference point (benchmark) and other points of interest.
Road and Railway Construction
In road and railway construction, dumpy levels are used to ensure the proper alignment and grade of the roads and tracks. By establishing accurate horizontal reference lines, surveyors can ensure that the roads and tracks are built with consistent slopes and grades, enhancing safety and efficiency.
Pipeline and Utility Installation
When laying pipelines, utility lines, or other underground structures, it’s crucial to maintain a uniform slope and elevation to ensure proper drainage and functionality. Dumpy levels aid in setting the appropriate gradient for these installations, preventing issues like water accumulation or improper flow.
Site Preparation and Earthwork
Before any construction project begins, the land needs to be properly prepared, which often involves excavation, grading, and leveling. Dumpy levels help in assessing the existing terrain’s contours and slopes, guiding the earthwork process to ensure the site is suitable for construction.
Monitoring Land Deformation
Dumpy levels are also used for monitoring the deformation of land, such as subsidence or settling. By comparing repeated measurements over time, surveyors can detect any changes in the land’s elevation, identifying potential stability issues.
Setting Benchmarks and Control Points
Dumpy levels are used to establish benchmarks and control points on the ground, providing reliable reference points for future surveys or construction work. These benchmarks serve as fixed elevations that can be referred to in subsequent projects.
Land Surveying and Boundary Determination
While dumpy levels are not typically used for measuring horizontal angles, they can still be employed in land surveying for establishing level lines over long distances. This can aid in determining approximate boundaries and assessing the lay of the land.
Construction Layout and Alignment
Before construction begins, dumpy levels help in accurately positioning structures like walls, columns, and other components. This ensures that everything is aligned according to the design plans.
Agricultural Drainage Planning
In agricultural contexts, dumpy levels are used to plan drainage systems, ensuring that fields have proper slope for water runoff and irrigation purposes.
Advantages of Using a Dumpy Level: In-Depth Explanation
A dumpy level is a fundamental surveying instrument that offers several advantages for various construction, engineering, and surveying projects. Its straightforward design and reliable functionality make it a valuable tool in the field. Here are the detailed advantages of using a dumpy level:
Simplicity and Ease of Use
Dumpy levels are known for their user-friendly design. They don’t require complex setups or extensive training to operate. Surveyors and engineers can quickly learn how to use a dumpy level, making it an accessible tool for professionals of all experience levels.
Accurate Horizontal Leveling
The primary function of a dumpy level is to establish accurate horizontal reference lines. It ensures that structures and features are built on level ground, minimizing issues related to imbalanced foundations and uneven construction.
Cost-Effective Solution
Compared to more advanced surveying instruments, dumpy levels are relatively affordable. This makes them a practical choice for smaller construction projects, site grading, and tasks that don’t demand the extreme precision of high-end instruments.
Versatile Terrain Compatibility
Dumpy levels can be used in various terrains, including flat areas, gentle slopes, and moderately uneven surfaces. As long as the leveling base is stable and properly set up, the dumpy level can provide accurate measurements.
Reliable Benchmark Establishment
Dumpy levels are crucial for setting up benchmarks and control points on construction sites. These benchmarks serve as fixed reference points for future surveys, ensuring consistency in measurements across different phases of a project.
Clear and Direct Readings
Dumpy levels typically have clear and well-defined crosshairs within the telescope, which aid in accurate readings of staff measurements. This feature contributes to the instrument’s reliability in obtaining precise data.
Suitable for Small to Medium-Scale Projects
For projects that don’t require extremely high precision or advanced surveying techniques, dumpy levels are an ideal choice. They are particularly well-suited for tasks like site preparation, foundation leveling, and basic road construction.
Robust and Durable Design
Dumpy levels are often built to withstand rugged outdoor conditions. Their sturdy construction allows them to endure the rigors of construction sites, making them dependable tools in challenging environments.
Quick Setup and Operation
Setting up a dumpy level is a straightforward process that involves leveling the instrument using the built-in leveling screws and tripod bubble level. Once set up, surveyors can begin taking measurements promptly.
Lesser Susceptibility to Vibration
In comparison to more complex instruments, dumpy levels are less sensitive to minor vibrations, which can be advantageous when working in environments where vibrations are present, such as near roadways or construction sites.
Dis-Advantages of Dumpy Level
While dumpy levels have their merits, they also come with certain limitations and disadvantages that should be considered before using them in surveying and construction projects. Here are the detailed disadvantages of using a dumpy level:
Limited Vertical Measurement Capability
One of the significant drawbacks of a dumpy level is its limited ability to measure vertical angles. It is primarily designed for horizontal leveling and does not provide accurate measurements for steep slopes or vertical height differences.
Dependence on Line of Sight
Dumpy levels require a clear line of sight between the instrument and the staff held at the target point. Obstructions such as trees, buildings, and other structures can hinder accurate measurements, especially in areas with restricted visibility.
Atmospheric Conditions Affect Accuracy
Adverse weather conditions like rain, fog, and haze can impact the visibility of the staff and the telescope’s crosshairs, leading to inaccurate readings. These conditions can limit the instrument’s effectiveness, particularly in outdoor environments.
Limited Application for Large-Scale Projects
Dumpy levels are best suited for small to medium-scale projects where a moderate level of accuracy is sufficient. For larger projects that demand high precision and extensive measurements, more advanced instruments like total stations or laser levels are more appropriate.
Not Suitable for Angle Measurement
Dumpy levels are primarily used for leveling and height determination, but they are not equipped to measure horizontal angles. Instruments like theodolites or total stations are necessary for tasks that involve measuring angles accurately.
Requires a Stable Setup Surface
To achieve accurate readings, a dumpy level must be set up on a stable and level surface. If the tripod or setup point is not properly leveled, it can lead to errors in measurements.
Manual Staff Reading Errors
Dumpy level measurements rely on reading staff markings through the telescope’s crosshairs. Human error, parallax, and misinterpretation of staff markings can introduce inaccuracies in measurements.
Inefficiency for Rapid Data Collection
The process of setting up a dumpy level, sighting the staff, and recording measurements can be time-consuming. In situations where rapid data collection is essential, other instruments with electronic data logging capabilities might be more efficient.
Lack of Digital Features
Traditional dumpy levels do not offer digital enhancements or data storage capabilities, which can hinder the efficiency of data management and analysis, especially in modern surveying workflows.
Unsuitability for High-Precision Work
For projects that require extremely precise measurements, such as advanced engineering or geodetic surveys, dumpy levels are not the optimal choice due to their inherent limitations in accuracy.
The Components of a Dumpy Level and Their Purposes
A dumpy level is a precision optical instrument used in surveying and engineering to establish horizontal lines and determine relative elevations. It consists of several essential components, each with a specific function. Here are the main parts of a dumpy level and their functions:
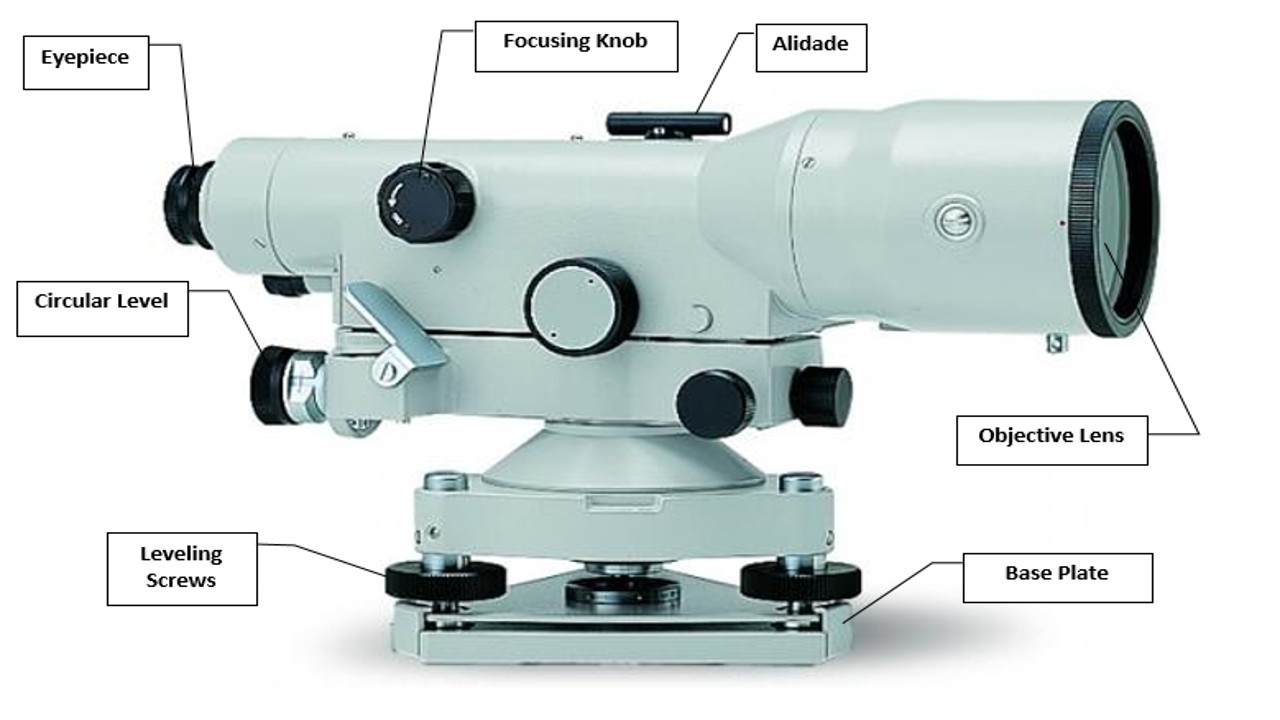
Telescope
The telescope is the primary optical component of the dumpy level. It is used to sight and observe the leveling staff or benchmark points.
Leveling Screws
Leveling screws are used to adjust and level the instrument. By turning these screws, the surveyor ensures that the telescope is perfectly horizontal, which is crucial for accurate measurements.
Vertical Axis
The vertical axis allows the telescope to rotate in a vertical plane. This rotation enables the surveyor to measure height differences between different points.
Horizontal Graduated Circle
Some dumpy levels have a horizontal graduated circle mounted on the instrument. It is used for measuring horizontal angles. However, this feature is not present in all dumpy levels, as they are primarily designed for leveling.
Tripod
The tripod provides support and stability for the dumpy level. It allows the instrument to be set up at a desired height and position while ensuring a secure base for accurate measurements.
Bubble Level
The bubble level, also known as a spirit level, is mounted on the dumpy level’s body or telescope. It helps the surveyor ensure that the instrument is set up on a level surface before taking measurements.
Crosshairs
Crosshairs are lines or marks inside the telescope’s eyepiece. They provide a reference point for aiming at the staff or benchmark, allowing the surveyor to make precise observations.
Focusing Mechanism
The focusing mechanism allows the surveyor to adjust the telescope’s focus to obtain clear and sharp images of the target points.
Eyepiece
The eyepiece is where the surveyor looks through the telescope. It contains the crosshairs and allows for accurate sighting of the staff or benchmark.
Base Plate
The base plate is the bottom part of the dumpy level where leveling screws are attached. It provides stability and support for the leveling mechanism.
Foot Screws
Foot screws are used to secure the dumpy level to the tripod. They ensure that the instrument is firmly mounted and aligned with the tripod’s vertical axis.
Objective Lens
The objective lens is located at the front of the telescope. It gathers light and forms the initial image of the target point for further observation through the eyepiece.
Sunshade/Rain Cover
Some dumpy levels come with a sunshade or rain cover to protect the telescope’s lenses from glare, direct sunlight, or adverse weather conditions.
Using a Dumpy Level for Surveying: Step-by-Step Guide
A dumpy level is a valuable tool in surveying for establishing horizontal reference lines and determining relative elevations. To use a dumpy level effectively, follow these detailed steps:
Choose a Suitable Location
Find a stable and level spot for setting up the dumpy level and tripod. Avoid areas with excessive vibrations or uneven ground.
Set Up the Tripod
Open the tripod legs and secure them firmly in the ground. Ensure that the tripod is level using the built-in bubble level.
Attach the Dumpy Level
Place the dumpy level onto the tripod’s head plate and secure it using the foot screws. Make sure the instrument is properly centered and aligned.
Rough Leveling
Adjust the leveling screws on the base plate to roughly level the dumpy level. Use the bubble level on the instrument to guide you. The bubble should be centered within its indicators.
Fine Leveling
Look through the telescope and adjust the leveling screws further to achieve perfect horizontal alignment. Ensure that the crosshairs are precisely horizontal.
Choose a Benchmark
Select a benchmark or a reference point with a known elevation. This could be a permanent benchmark, a marked point, or a leveled staff held vertically.
Staff Reading
Have an assistant hold a leveling staff at the benchmark. The staff should be held vertically, and the assistant should position it so the bottom is touching the ground.
Take a Backsight Reading
Look through the telescope and focus on the staff. Align the crosshairs with a clearly visible mark on the staff. Read and record the staff reading.
Move to Target Points
Move the dumpy-level to other points where you want to determine relative elevations. Set up the instrument as before and level it accurately.
Take Fore-sight Readings
Have the assistant hold the staff at the target points. Look through the telescope and align the crosshairs with the staff. Read and record the staff reading for each point.
Calculate Height Differences
Calculate the height differences between the benchmark and the target points by subtracting the backsight reading from each foresight reading. This gives you the relative elevation values.
Repeat as Needed
Repeat the process for additional target points to create a profile of the terrain’s elevation changes.
Stadia Measurement (Optional)
If your dumpy-level has a stadia reticle, you can use it to directly measure distances by reading the staff markings. This requires additional calculations based on the stadia constants.
Record and Document
Document all measurements, including the benchmark’s elevation and the relative elevations of the target points. Use field notes, sketches, or digital tools to organize your data.
Pack Up
Once you’ve completed your measurements, carefully detach the dumpy-level from the tripod and pack it securely for transport.
Source: Civiconcepts – Bhushan Mahajan
Conclusion
Dumpy levels are essential tools in surveying and engineering for establishing horizontal lines and determining relative heights. While they have limitations, they offer simplicity and accuracy for various applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can a dumpy-level measure vertical angles?
No, dumpy-levels are primarily used for horizontal leveling.
What’s the difference between a dumpy-level and a theodolite?
A theodolite can measure both horizontal and vertical angles, making it more versatile than a dumpy-level.
Are dumpy-level suitable for building skyscrapers?
No, skyscraper construction requires more precise instruments like total stations.
How do I protect a dumpy-level in adverse weather?
Cover it with a weather-resistant material when not in use.
Can one person operate a dumpy-level?
Yes, one person can set up and operate a dumpy-level.
Can I use a dumpy-level in a forested area?
Dense vegetation might obstruct sightlines, affecting accuracy.
What’s the purpose of leveling screws on a dumpy-level?
Leveling screws help ensure the instrument is set up horizontally.
Are dumpy-levels digital nowadays?
Yes, modern versions might have digital enhancements for easier readings.
Can a dumpy-level replace a GPS for surveying?
No, GPS offers greater accuracy and efficiency for large-scale surveys.
How often should I calibrate my dumpy-level?
Calibrate it whenever you notice a decrease in accuracy or after significant impacts.






